Visual Abstract
Abstract
Hyperthyroidism is often managed with radioactive iodine therapy. The dose of 131I administered to the patient is based on the calculated size of the thyroid gland in grams and 24-h iodine uptake. Ultrasonography is a validated modality for determination of thyroid volume. Though necessary for assessing the degree of 123I uptake, nuclear scintigraphy also allows for estimating thyroid volume. Here we compare volume measurements calculated on the basis of ultrasonography and nuclear scintigraphy in a cohort of hyperthyroid patients. Methods: This prospective study was designed to evaluate 110 consecutive hyperthyroidism patients who were undergoing thyroid ultrasonography and 123I scintigraphy. Scintigraphy was performed after oral administration of approximately 11 MBq of 123I-sodium, and uptake at 2 and 24 h was measured. At 24 h, thyroid scintigraphy was performed using a nuclear medicine camera with a low-energy high-resolution collimator next to the patient’s chin. Thyroid measurements were calculated via the formula for determining a prolate ellipsoid. The formula was modified for radioactive iodine uptake because it is a planar image. Volumes calculated with these 2 modalities were subsequently analyzed and compared by linear regression. All patients had undergone ultrasonography at an average of 3 mo from nuclear scanning. All our patients’ 131I dosages were based on the thyroid measurements obtained by thyroid scintigraphy. Results: We included 110 patients (95 women, 15 men) with an age range of 20–95 y and an average age of 56 ± 17.4 y. Diagnoses included 66 cases of nodular goiter and 44 of Graves disease. There was a linear relationship between measurement of thyroid gland weight by the 2 modalities, which can be explained in the following formula: log US (g) = 0.84 + [0.65 × log NM (g)], where NM is thyroid scintigraphy and US is ultrasonography. Conclusion: We have validated that this method has helped obtain more accurate measurements of the thyroid gland by thyroid scintigraphy. Additionally, we have derived factors that convert the estimated thyroid volume calculated from thyroid scintigraphy to the expected ultrasonography value.
- Graves disease
- toxic nodular goiter
- antithyroid medication
- thyroid scintigraphy
- thyroid ultrasound
- radioactive iodine therapy
Hyperthyroidism is one of the most common endocrine disorders in the United States, affecting more than 1 in 100 people (1). Thyrotoxicosis describes the syndrome that occurs secondary to systematically elevated thyroid hormone levels and is characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, heat intolerance, tremor, and weight loss, among others (2). The 2 major causes of hyperthyroidism are Graves disease and toxic nodular goiter (3,4), whereas Hashimoto thyroiditis accounts for most cases that occur as a result of passive release (5). These hyperthyroid conditions are diagnosed with the aid of thyroid scintigraphy, also known as thyroid scanning or radioactive iodine (RAI) uptake (6).
Per the American Thyroid Association, there are 3 clinical options for treating hyperthyroidism: antithyroid medication, surgical thyroidectomy, and RAI treatment (7). Importantly, treatment with RAI is feasible only in the context of thyroid hormone overproduction, such as Graves disease or toxic multinodular goiter.
Hyperthyroidism is generally treated in a stepwise fashion and begins by achieving a euthyroid state with antithyroid medication (8). Although antithyroid medication such as methimazole and propylthiouracil can be effective in achieving euthyroidism in hyperthyroid patients, this treatment is not a definitive approach to treating hyperthyroidism (9,10). The remission rate after a standard 12–18 mo of treatment is only 50%–55%, with some patients requiring antithyroid medication for up to 6 y if used as the sole method of treatment. Thus, in the event of recurrence after an antithyroid medication regimen, which has been shown to occur in over 52% of patients, either RAI or surgical thyroidectomy is recommended (11).
Surgical thyroidectomy is a highly effective treatment but is indicated in only certain circumstances. These indications include abnormal cytology on fine-needle aspiration, very large goiters, goiters that cause airway obstruction or dysphagia, and pregnancy (12). In the absence of these indications for surgical thyroidectomy, RAI treatment is the definitive treatment of choice if antithyroid medication proves ineffective. RAI is especially used in postmenopausal women and male patients, as there is no risk of fetal abnormalities as there is in fertile female patients who may unwittingly be pregnant at the time of treatment (13).
For the past 80 y, since Saul Hertz first applied 131I as a treatment for hyperthyroidism in 1941 (14), RAI therapy has been the most commonly used definitive treatment for hyperthyroidism (15,16). The dose of 131I administered to the patient is determined by 2 factors: the percentage of 123I uptake in the thyroid at 24 h of an RAI uptake study and the calculated size of the thyroid gland in grams (17). For the calculation of the thyroid mass in grams, the density of the thyroid is generally assumed to be 1 g/cm3 (18). More specifically, the equation for 131I dose calculation (converted to MBq) in RAI is (17)…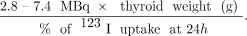 As such, it is crucial to be able to determine the weight of the thyroid with great accuracy in order to establish a safe and effective dose for RAI.
As such, it is crucial to be able to determine the weight of the thyroid with great accuracy in order to establish a safe and effective dose for RAI.
Ultrasonography is a validated modality for determining thyroid volume (19,20). Though necessary for assessing the degree of 123I uptake in RAI uptake studies, nuclear scintigraphy also allows for estimating thyroid volume. This study compared volume measurement calculations based on ultrasonography and nuclear scintigraphy in a cohort of patients with hyperthyroidism.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2018 to December 2019, this prospective study evaluated 110 consecutive hyperthyroid patients, all of whom had undergone thyroid ultrasonography and 123I scintigraphy within 1 d to 6 mo of each other (91 d on average). Institutional review board approval for review of the patients’ records was obtained. However, consent forms were not obtained from patients because thyroid ultrasonography is a routine evaluation for all hyperthyroid patients to rule out thyroid malignancy before potential 131I therapy. Patients with a clinical diagnosis of hyperthyroidism and elevated results on thyroid function tests were referred. Patients with a diagnosis of thyroid carcinoma were excluded. Thyroid imaging was performed at 24 h after administration of approximately 11.1 MBq of 123I-sodium in anterior, left anterior oblique, and right anterior oblique views. Patients lay supine with the neck extended and were imaged at the level of the chin using a Millennium camera with low-energy high-resolution parallel-hole collimators (GE Healthcare) to best evaluate the thyroid gland dimensions. In patients with a normal or high count rate, the images were obtained for 35,000 counts. In patients with a low count rate, a 10-min image was obtained. Ultrasonography was conducted using dedicated IU 22 ultrasonography L12-5 linear transducers (Philips). Thyroid lobe volumes from ultrasonography were calculated by 0.5 × length × width × depth. This formula was derived from the geometric method for calculating the volume of a prolate ellipsoid (21). In a similar fashion, thyroid lobe volumes from 123I scintigraphy were calculated by 0.5 × length × width × width. The volumes of both lobes and, if present, that of the isthmus were added together, resulting in the total thyroid volume. Representative images used for thyroid volume estimation for both Graves disease and multinodular goiter are shown in Figures 1 and 2, respectively. All thyroid scintigraphy and calculations were reviewed and analyzed by 3 experienced nuclear medicine physicians. All ultrasonography was performed and reviewed by the expert radiologists in the Radiology Department. Volumes calculated with these 2 modalities were subsequently analyzed.
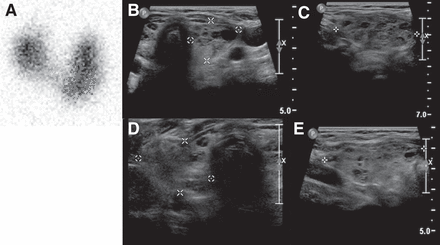
Planar 123I scintigraphy imaging and ultrasonography of patient with Graves disease. (A) Thyroid scintigraphy (right lobe, 6.19 × 2.52 cm; left lobe, 6.48 × 25.4 cm). (B) Ultrasonography, left lobe (length × width, 6.4 × 1.7 cm). (C) Ultrasonography, left lobe (depth, 2.7 cm). (D) Ultrasonography, right lobe (length × width, 5.9 × 1.8 cm). (E) Ultrasonography, right lobe (depth, 2.4 cm).
Planar 123I thyroid scintigraphy and ultrasonography of patient with multinodular goiter. (A) Thyroid scintigraphy (right lobe, 5.4 × 2.9 cm; left lobe, 4.3 × 2.4 cm). (B) Ultrasonography, left lobe (length × width, 5.1 × 2.0 cm). (C) Ultrasonography, left lobe (depth, 2.4 cm). (D) Ultrasonography, right lobe (length × width, 5.2 × 1.7 cm). (E) Ultrasonography, right lobe (depth, 2.5 cm).
Paired t testing was used to compare the thyroid gland weight between the ultrasonography and the thyroid scintigraphy. Pearson correlations were calculated between the thyroid gland weights measured by ultrasonography and thyroid scintigraphy. Linear regression models were used to explore the relation between measurement of thyroid gland weight by the thyroid scintigraphy and ultrasonography. To achieve normality, reduce variability, and fit the model better, logarithm transformations were used for measurements by the thyroid scintigraphy and ultrasonography in the linear regression model. All statistical analyses were done using Stata, version 17.0 (StataCorp LLC).
RESULTS
We included 110 patients (95 women, 15 men) with an age range of 20–95 y and an average age of 56 ± 17 y. Diagnoses included 66 cases of nodular goiter and 44 of Graves disease. The mean thyroid gland weights for patients with Graves disease were 33.1 ± 50.1 g via ultrasonography measurement and 50.0 ± 45.6 g via thyroid scintigraphy (P = 0.001).
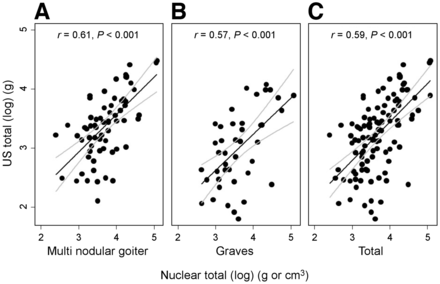
For patients with a nodular goiter, however, the mean thyroid weight calculated by ultrasonography measurement was 34.1 ± 18.9 g whereas the thyroid scintigraphy method resulted in a mean of 47.8 ± 28.7 g (P < 0.001). In both Graves and nodular goiter patients, there was a good correlation between measurements by thyroid scintigraphy and by ultrasonography (r = 0.8327 and r = 0.7174, respectively; P < 0.001). The overall correlation coefficient regardless of diagnosis was 0.7804 (P < 0.001). There was a linear relationship between measurement of thyroid gland weight by the 2 modalities (regardless of diagnosis), as can be explained in the following formula: US (g) = 0.84 + [0.65 × log NM (g)], where NM is thyroid scintigraphy and US is ultrasonography (r = 0.59, P < 0.001 for the slope; Fig. 3C). Moreover, there are separate linear relationships between measurement of thyroid weight between the 2 modalities with respect to the diagnosis of either Graves disease or nodular goiter.
(A) Linear relationship between volume estimations from log US (g) and log NM (g) in patients with nodular goiter. (B) Linear relationship between volume estimations from log US (g) and log NM (g) in patients with Graves disease. (C) Linear relationship between volume estimations from log US (g) and log NM (g) from all patients included in study, regardless of diagnosis as nodular goiter or Graves disease.
For Graves patients, log US (g) = 0.77 + [0.62 × log NM (g)] (r = 0.57, P < 0.001; Fig. 3B), whereas for nodular goiter patients, log US (g) = 1.03 + [0.63 × log NM (g)] (r = 0.61, P < 0.001; Fig. 3A). Figure 3 shows that the relationship holds up better for thyroid glands of 20–55 g (exp3 to exp4), with a narrowed 95% CI. Linear regressions for log US (g) using log NM (g) as a predictor are shown in Table 1 by diagnosis and for all patients.
Linear Regression for Log US (g) Using Log NM (g) as Predictor by Diagnosis
Figure 1 depicts both the 123I thyroid scintigraphy and the thyroid ultrasonography for a 27-y-old woman with hyperthyroidism. The thyroid scintigraphy showed uniform uptake throughout the enlarged lobes of the thyroid gland, consistent with Graves disease. Thyroid uptake at 2 h was 26.5% (range, 5%–10%) at 2 h and 62.2% (range, 10%–35%) at 24 h. Ultrasonography showed bilaterally enlarged lobes with no nodules.
Figure 2 depicts both the 123I thyroid scintigraphy and the thyroid ultrasonography for an 89-y-old woman with hyperthyroidism. The thyroid scintigraphy showed nonuniform uptake in the right lobe of the gland, consistent with multinodular goiter. Thyroid uptake was 4.2% (range, 5%–10%) at 2 h and 16.3% (range, 10%–35%) at 24 h, consistent with subclinical hyperthyroidism. Ultrasonography showed bilaterally enlarged glands with a nodule in the right upper pole.
DISCUSSION
Here, we have shown the ability to obtain accurate thyroid volume measurements through planar 123I scintigraphy and imaging with a γ-camera using a high-resolution parallel-hole collimator. We used a modified ellipsoid formula based on dimensions obtained from a single anterior view, as well as a modified acquisition protocol characterized by placing a wide-view γ-camera at the patient’s chin with the neck in hyperextension. We reasoned that these changes would aid in curtailing the volume overestimations that we had previously seen with scintigraphy at our institution. The ability to assess thyroid volume via scintigraphy has been well investigated and previously reported (22–24). However, the standard methodologies for estimation generally result in inaccuracies in measurement—either underestimating or overestimating the volume depending on the formula and the architecture of the gland (22). Ultrasonography has been shown to estimate volume more accurately and, for this reason, has generally been adopted as the gold standard imaging modality for volume estimation before RAI therapy (23,25,26).
To improve the accuracy of scintigraphy-based volume estimations, linear regression was used to compare scintigraphically obtained volumes with ultrasonographically obtained volumes. Regression analysis revealed a fairly strong linear relationship between the volumes derived from ultrasonography with those derived from scintigraphy (Fig. 3C). Importantly, this relationship allowed for derivation of a correction factor such that scintigraphically obtained volumes could be corrected to align more closely with volumes obtained ultrasonographically. This correction factor—which in our study predominantly corrected for the overestimation of scintigraphy relative to ultrasonography—allows for accurate volume estimation with scintigraphy alone (Figs. 3A–3C). Importantly, this estimation can be made more accurate by stratifying patients by Graves and nodular goiter, as the slopes of the regression lines obtained differ between these 2 patient cohorts (Figs. 3B and 3C). This, in turn, could streamline the preprocedural workup in patients awaiting radioiodine therapy, as scintigraphy could be used to determine radioiodine uptake and thyroid volume simultaneously. Although ultrasonography is generally considered accessible and cost-effective (24), scintigraphy is a requirement before RAI therapy. Extending its role to estimate volume in addition to radioiodine uptake would spare patients an additional test—a net gain to both patients and the health-care staff treating them.
Currently, there is debate on whether hyperthyroidism is better treated with standardized or calculated doses of 131I. Treatment with standardized doses is based on general size (small, medium, or large) and applies a 185-, 370-, or 555-MBq dose of 131I, respectively. Calculated doses use a formula that accounts for thyroid weight and RAI to determine the treatment dose. Peters et al. determined that outcomes are dependent on the radiation dose absorbed, which is inversely proportional to thyroid size (26). As such, patients with standardized doses had lower treatment success in larger thyroid goiters than patients who received calculated doses. Although an additional study found the 2 methods to be equally effective, this study did not take into account differences in thyroid volume (27). Furthermore, with the importance of personalizing treatments to the patient’s own gland size, nodularity, treatment history, and longevity of illness, using a set dose for all patients may not adequately treat the patient or may expose patients with smaller thyroids to unnecessary levels of radiation. Therefore, taking into account each patient’s thyroid volumes and diagnoses helps to individualize treatment.
Although our methodology improves volume estimation via scintigraphy, the methodology itself requires that a series of previous ultrasonography measurements be available on which regression analysis can be performed. For this reason, volume estimation using this correction factor suffers from the limitations inherent in ultrasonography: a tendency to underestimate volume and a lack of precision relative to slightly more robust modalities such as CT and MRI (25,28,29). Although CT and MRI have shown superior performance in volume estimation, both have shortcomings. MRI is expensive and time-consuming, whereas CT increases exposure to unnecessary radiation. The negative aspects of these 2 imaging modalities, relative to ultrasonography, make them less desirable in preprocedural thyroid volume estimations. It is generally uncommon for CT and MRI to be used as stand-alone modalities for estimation of thyroid volume. When these modalities are used for thyroid evaluation, it is usually in response to an incidental finding (30) such as was demonstrated in our study, in which only 3 of the 110 subjects had undergone CT specifically to evaluate the thyroid. Though reports from these 3 scans commented on the heterogeneity and overall appearance of the thyroid, only 1 of these scans reported a thyroid measurement for comparison with ultrasonography and scintigraphy. No patients underwent MRI specifically for evaluation of the thyroid—all thyroid evaluations stemmed from incidental findings on studies ordered for alternative indications. Thus, although some in the field have shown CT and MRI to be the most accurate modalities in thyroid volume determination, our institution did not have available the data needed to create a correction factor to convert volumes obtained via thyroid scintigraphy to more closely align with measurements obtained via CT and MRI (28). The task of creating such a correction factor should be further investigated at an institution in which thyroid volume estimations by CT and MRI are more commonplace.
CONCLUSION
The thyroid gland can be measured accurately using a γ-camera with a low-energy high-resolution parallel-hole collimator and by positioning patients accurately. Through this technique, we have validated thyroid scintigraphy as an accurate modality for determining thyroid weight before decision making in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. Additionally, we have derived conversion factors with which the estimated thyroid volume calculated from thyroid scintigraphy can be converted to the expected ultrasonography value. These conversion factors provide physicians with the potential to streamline the treatment pathway for patients with hyperthyroidism by obviating ultrasonography thyroid volume estimation before the RAI uptake study.
DISCLOSURE
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
KEY POINTS
QUESTION: Can 123I thyroid scintigraphy be used to accurately assess thyroid volumes before treatment with 131I-sodium?
PERTINENT FINDINGS: Thyroid volumes calculated with ultrasonography and thyroid scintigraphy showed a statistically significant linear relationship, creating a formula conversion factor that can accurately assess for thyroid weight using scintigraphy alone.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PATIENT CARE: Using an already-needed 123I scan to evaluate both uptake values and thyroid volumes gives physicians the potential to remove the need for additional ultrasonography before treatment. This change would not only streamline the treatment process but also improve the cost effectiveness of hyperthyroidism management, as well as decreasing the financial and temporal burden on patients.
Footnotes
Published online May. 24, 2022.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication October 29, 2021.
- Revision received March 22, 2022.