Visual Abstract
Abstract
Radioiodine therapy has been widely used for ablation of remnant tissue after surgical treatment of differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC). Internal dosimetry provides a new approach to choosing the administered activity—an approach that considers the distribution and retention of 131I individually per patient. This study used clinical techniques of internal dosimetry to assess the accumulated activity, internal bone marrow dosimetry, and effective half-life in patients undergoing treatment for DTC. Methods: This was a quantitative, retrospective study analyzing diagnostic documents and images. The internal dosimetry method calculated the dose absorbed by the bone marrow per administered activity of 131I. Calculation of the absorbed dose took into account the accumulated activity, which was obtained through measurements of whole-body images acquired at 4 intervals over 5 d. Results: The median dose absorbed by the bone marrow per administered activity was 0.117 mGy/MBq (range, 0.043–0.152 mGy/MBq). The median whole-body residence time was 22.0 h (range, 12.6–39.4 h). The median effective half-life was 15.6 h (range, 7.6–28.2 h). Conclusion: Internal dosimetry provides information relevant to safe dose limits for DTC radioiodine therapy, especially in advanced cases of the disease for which greater activities may be necessary.
Thyroid cancer is the most common cancer of the head and neck region and affects 3 times as many women as men. The most indicated treatment for differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) is partial or total thyroidectomy, complemented by radioactive iodine therapy (1). This treatment is indicated because DTC and its metastases maintain the biologic characteristics of a healthy thyroid, including the expression of sodium iodide transport protein, the main cell responsible for specific iodine uptake (2). Thus, radioiodine therapy is indicated for ablation of remaining tissue that is not resected or is incompletely resected. For thyroid disease, 131I-NaI is currently the most common radionuclide treatment (3).
In ablation of remnant thyroid tissue after surgery, the activity of 131I-NaI usually prescribed is between 1 and 5 GBq in a single administration and may be higher in more advanced cases of the disease (2). These amounts of activity have been selected empirically, with no consensus, varying between authors and nuclear medicine centers that perform this therapeutic procedure (4).
When fixed activities are considered, the accumulated activity, and hence the absorbed dose, is not thought to change considerably from patient to patient. The characteristics that alter iodine distribution are age, sex, renal function, and injury extent, among others (5). The administered activity is individualized through therapeutic planning using dosimetric procedures. Internal dosimetry provides information on the distribution of iodine in a patient’s body, allowing estimation of the activity to be used and preventing the biologic effects of ionizing radiation (6).
This study assessed accumulated activity, internal bone marrow dosimetry, and effective half-life using clinical internal dosimetry techniques in patients undergoing treatment for DTC.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study retrospectively assessed pretherapeutic internal dosimetry in 5 patients who were diagnosed with DTC and were undergoing total or quasi-total thyroidectomy. Dosimetry was used as a strategy to plan radioiodine therapy for ablation of remnant tissue and metastases. The study was conducted in a private nuclear medicine service in southern Brazil. The research was submitted to a Brazilian ethics committee for evaluation, receiving approval 3.988.505. Written informed consent was obtained from each patient before participation in the study. Three internal dosimetry techniques were available for radioiodine therapy, one or all of which could be chosen, depending on the indication: bone marrow–based dosimetry, lung-based dosimetry, or organ-based dosimetry. All used diagnostic images to determine the accumulated activity.
Preparation of patients for dosimetry reproduced preparation for therapy: restriction of foods that contain iodine, and suspension of medications and preparations that contain iodine (up to 4 wk). In 4 cases, hormonal suspension was performed, and in one case, recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone was used. A choice between the 2 methods was needed because of the need to reproduce the anticipated therapy method. Some authors have shown that residence time can be different between hormone withdrawal and the use of recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone (7,8).
Acquisition of Whole-Body Images
An oral 131I-NaI solution with 74 MBq of activity was administered. The activity was measured with a CRC-15R radioisotope dose calibrator (Capintec, Inc.). Afterward, whole-body conjugate images were acquired using a Symbia T2 SPECT/CT γ-camera (Siemens). The equipment has 2 detectors with a 15.875-mm (5/8 in) NaI:Tl crystal and is equipped with high-energy collimators, which are required because of the photon energy of 131I (364 keV). The acquisition mode was a whole-body scan, and the table speed was 12 cm/min.
Four images were acquired, one each at 2, 6, 48, and 120 h after tracer administration, with the patient not emptying the bladder before the first image. Thus, the whole-body count of the 2-h image was considered to be 100% of the administered activity.
For image acquisition, the triple-energy-window method was used to correct the scatter due to 131I γ-radiation energy and use of a high-energy collimator (9,10). With 3 energy windows simultaneously, the 15% main window was centered on the 364-keV (range, 336.7–391.3 keV) photopeak and 2 windows of 6%, one below and one above the main window, at 314.9–336.7 keV and 391.3–413.1 keV, respectively.
Data Processing
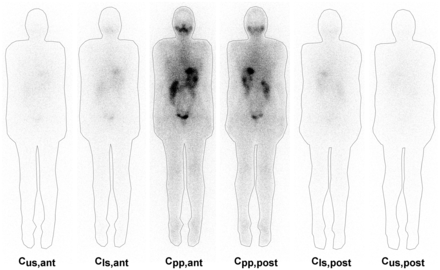
The acquired images were exported in DICOM format and assessed in ImageJ processing software (National Institutes of Health). Each acquired image series, per interval, consisted of 6 images: anterior and posterior, scattering in the inferior anterior and posterior windows, and scattering in the superior anterior and posterior windows. In each image, a region of interest was drawn outlining the patient’s whole body. For the region of interest, the total counts were measured and the values were recorded as Cpp,ant, Cpp,post, Cls,ant, Cls,post, Cus,ant, and Cus,post (where C is total counts, ant is anterior, post is posterior, pp is photopeak, ls is lower scatter window, and us is upper scatter window) as shown in Figure 1.
Measurement of regions of interest of set of anterior and posterior conjugate images and their respective images for scattered radiation correction.
The triple-energy-window scatter fraction determination is described in Equation 1, considering the measured counts for images with the energy window shifted below (Cls) and above (Cus) (9): Eq. 1where Wpp is the width centered on the photopeak window, Wus is the width of the lower window, and Wup is the width of the upper window.
Eq. 1where Wpp is the width centered on the photopeak window, Wus is the width of the lower window, and Wup is the width of the upper window.
The total count is the result for the image counts, with the main energy window (Cpp) subtracted from the total scattering (Cscatter) (2). Both counts are the geometric mean of the anterior and posterior projections: Eq. 2
Eq. 2
Accumulated Activity Determination
The total counts for each image set (at 2, 6, 48, and 120 h) were plotted on a chart, and the time–activity curve was determined. The curve adjustment results in an equation of the double-exponential format: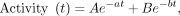 Eq. 3
Eq. 3
where A, B, a, and b are curve adjustment coefficients; t is time; and e is Euler's number (a numerical constant).
The accumulated activity (Ã) is the total number of disintegrations over a period and is determined by activity integration by time (Eq. 4). In the activity chart by time, the accumulated activity is determined by the area below the curve: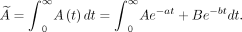 Eq. 4
Eq. 4
Alternatively, the concept of residence time can be used, as well as the accumulated activity per administered activity.
Absorbed Dose Estimation
The absorbed dose to the bone marrow is calculated by an adaptation of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine protocol (11) in which a sample of blood is not used. The assessed compartment is blood, considering that the activity concentration in blood and bone marrow is similar (12). For this symmetric approach, 2 components are assessed: blood self-irradiation and blood irradiation by 131I concentration in the whole body. The absorbed dose to the bone marrow per unit of activity administered is defined by the sum of these 2 components: Eq. 5where D is the absorbed dose, A0 is the administered activity, S is the mean absorbed dose per unit of accumulated activity, and τ is residence time. The Sblood←blood value, using β-radiation decay, is 108 Gy⋅mL/GBq⋅h. The component for the dose coming from the whole body, Sblood←body, is 0.0188⋅m−2/3 Gy/GBq⋅h, which depends on the body mass (m) (11). S values replaced in Equation 5 are described in Equation 6:
Eq. 5where D is the absorbed dose, A0 is the administered activity, S is the mean absorbed dose per unit of accumulated activity, and τ is residence time. The Sblood←blood value, using β-radiation decay, is 108 Gy⋅mL/GBq⋅h. The component for the dose coming from the whole body, Sblood←body, is 0.0188⋅m−2/3 Gy/GBq⋅h, which depends on the body mass (m) (11). S values replaced in Equation 5 are described in Equation 6: Eq. 6
Eq. 6
The first component, Dblood←blood, is traditionally measured by the blood sample density counts over time (11). In 2009, Hänscheid et al. (13), through the considerations initially made by Thomas et al. in 1993 (14), proposed determination of Dblood←blood exclusively through analysis of body residence time, that is, blood residence time is determined indirectly. In their studies, blood residence time represents 14% ± 3% of body residence time. Therefore, the proposed relationship can be expressed as follows: Eq. 7
Eq. 7
BV, the blood volume in milliliters, is expressed in Equation 8 for men and in Equation 9 for women (15):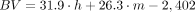 Eq. 8
Eq. 8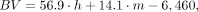 Eq. 9
Eq. 9
where h is height in centimeters and m is mass in kilograms.
Equations 6 and 7 can be combined and expressed as Equation 10, which was used to determine the total absorbed blood dose: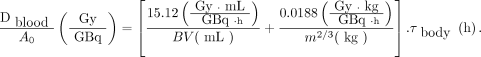 Eq. 10
Eq. 10
Comparatively, Dblood/A0 (dose in blood per administered activity) was calculated using OLINDA/EXM, version 1.0 (Vanderbilt University). In the software, 131I was selected as the radionuclide, and the phantom was chosen between a woman and a man. In biokinetic data entry, body residence time was used for the whole body (total body/remainder of body), and blood residence time was used for the bone marrow (red marrow); however, because blood residence time was calculated to 1 mL, it was necessary for it to be multiplied by the organ mass. For the phantom used, the bone marrow mass was 1,300 and 1,120 g for women and men, respectively.
Maximum Activity
Bone Marrow
The maximum activity is determined by Equation 11. A maximum dose of 2 Gy was used, considering the bone marrow as the target organ. Bone marrow is the critical organ in radionuclide therapy. In dosimetry studies, alterations in the hematopoietic system have been observed in a subgroup that received doses higher than 2 Gy to the bone marrow (16). Eq. 11
Eq. 11
The maximum activity was also evaluated for a maximum dose of 1.3 Gy, considering the uncertainties in the measurement method without the use of a blood sample (13).
Lung
When there was diffuse pulmonary metastasis, the maximum administered activity was determined with consideration that lung activity after 48 h is not higher than 2.96 GBq (17–19). A region of interest was drawn for the lungs, and count density was measured in the conjugated images and applied to the scattering correction as the whole-body region of interest. Count density in the lungs after 48 h (Clung,48 h) was compared with the whole-body density counts of the 2-h image (Ctotal,2 h):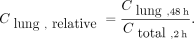 Eq. 12
Eq. 12
The maximum activity of administered 131I-NaI to prevent radiation effects is determined as follows: Eq. 13
Eq. 13
Effective Half-Life
The activity concentration in a patient’s body depends on the physical and biologic half-life of 131I. The physical half-life is 8.02 d, whereas the biologic half-life varies with the individual, depending on multiple variables. Through analysis of accumulated activity, the activity curve as a function of time was calculated for each patient.
Organ-Based Dosimetry
To compare the bone marrow toxicity limit with the activity needed to treat a thyroid remnant, one patient was selected for dosimetry based on the injury. The absorbed dose in the organ was compared with the administered activity using the total-volume dosimetry method (20,21).
The SPECT/CT acquisition for dosimetry used 60 projections (30/detector), 6 steps, 60 s, a 128 × 128 matrix, and a triple-energy window. Iterative ordered-subsets expectation maximization was used for reconstruction, with 10 iterations and 5 subsets.
Partial-volume effect correction was experimentally determined using an image-quality International Electrotechnical Commission 61675-1 simulator. Spheres that were 28.7, 16.8, 8.6, 3.6, 2.1, and 1.1 mL in volume were filled with a constant 131I concentration, and the recovery coefficient was projected. The recovery coefficient determines the correlation between differences in the actual and measured values of both activity and volume: Eq. 14
Eq. 14
where RC = recovery coefficient, [A]measured is the measured activity concentration, [A]actual is the actual activity concentration, v0 is the object’s actual volume, va is the apparent volume, cm is the measured count density, and c0 is the actual count density. The apparent volume was measured in the image, with a volume of interest positioned on the structure with a threshold of 5%, and determined as follows: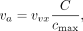 Eq. 15where vvx is the voxel volume, C is the count density measured in volume of interest, and Cmax is the highest-intensity voxel count density.
Eq. 15where vvx is the voxel volume, C is the count density measured in volume of interest, and Cmax is the highest-intensity voxel count density.
The accumulated activity is determined by assessing the 131I concentration over time by means of a sequence of SPECT images used in bone marrow dosimetry. The activity for each image series is determined as follows: Eq. 16
Eq. 16
where Ai is the activity measured for each interval, C is the total count with a threshold of 30% of the image, f30 is the measurement correction factor in a threshold of 30% to 5%, and ε is the activity calibration factor per count (MBq/count) experimentally determined for imaging equipment with a volume with known activity. f30 is needed to use a 30% threshold for target area measurement, avoiding the interference of background radiation in the target volume.
Equation 17 describes the absorbed dose in the sphere, as determined by the product sphere residence time. S value is calculated for the actual sphere volume corrected by tissue density: S = 0.110⋅vsphere−0.974 Gy/MBq⋅h and ρ = 1.05 g/cm3 (20). Eq. 17
Eq. 17 Eq. 18
Eq. 18
RESULTS
Internal dosimetry had, as an indication, cases of advanced disease and cases in retreatment with suspicion or confirmation of metastases. Table 1 lists the sex, age, height, mass, body mass index, and estimated body blood volume of the assessed group, as well as total-body residence time and blood residence time. The residence time for the whole body was a median of 22.0 h.
Variables for Internal Dosimetry Cases
Count density behavior over time is illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 2 illustrates the time–activity curve of the assessed group. Curve adjustment coefficients were obtained through the fit-data application of OLINDA/EXM.
Time–activity fitted curves for assessed patients. P1–P5 = patients 1–5.
Bone Marrow–Based Dosimetry
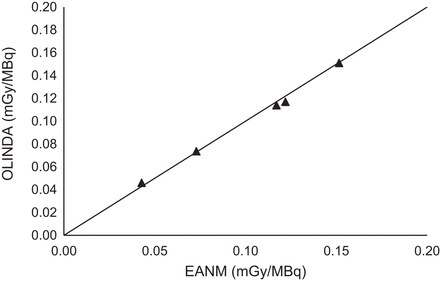
Dose in blood per administered activity was determined with body residence time and blood residence time using an adaptation of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine protocol without blood sampling (Eq. 10) and OLINDA/EXM. The methods did not significantly differ when analyzed by a paired t test (P = 0.564).
Figure 3 compares OLINDA/EXM and the European Association of Nuclear Medicine protocol. The individual and maximum doses in blood per administered activity, considering red bone marrow toxicity of 2 Gy and 1.3 Gy, are expressed in Table 2.
Comparison of absorbed dose by activity calculated by OLINDA/EXM and EANM.
Maximum Activity for Assessed Case Group
Table 3 presents the time required for decay of half or a quarter of the initial activity, both effective and biologic. The median time of the first effective half-life was 15.6 h (range, 7.6–28.2 h), and the second half-life was 12.8 h (range, 5.5–24.9 h). Patient 3 was prepared with recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Effective and Biologic Times for Half and Quarter of Initial Activity of 131I
Lung Dosimetry
One patient had pulmonary metastasis. Relative count density in the lungs was 0.0246; that is, after 48 h, 2.46% of the iodine concentration was retained in the lung compared with the whole-body measurement measured in the 2-h image. Therefore, the maximum calculated activity was 120.5 GBq. Maximum activity based on dose limits in bone marrow and lung were compared, with the lowest prevailing. The dosimetry for this case, considering the dose limit of 2 Gy in the bone marrow, determined the maximum activity of 27.4 GBq. Thus, the limit for the bone marrow was prioritized.
Organ-Based Dosimetry
The activity ratio measured by the actual activity designated as recovery coefficient is expressed in Figure 4.
Recovery coefficient of definitive experiment. ● = apparent volume; × = true sphere volume.
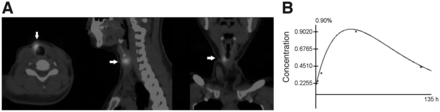
The dosimetry for one patient (patient 5) in the studied group was assessed. The injury was characterized as remaining tissue in the thyroid bed, illustrated in Figure 5A. The volume was estimated at 1.9 cm3. Factor f30 was determined at 0.59 for a point source illustrated in Figure 5A, and the equipment ε calibration factor was calculated at 15,604 counts/MBq. The residence time was calculated at 0.995 h; the time–activity curve is expressed in Figure 5B. Through residence time, volume, and S value, the dose absorbed by the organ per unit of 131I administered was 0.0584 Gy/MBq, calculated by Equation 17. Considering the dose of 300 Gy necessary to ablate the remaining thyroid tissue, proposed by Maxon et al. (22), the administered activity required to reach this dose threshold would be 4.89 GBq. The maximum 131I activity to prevent bone marrow toxicity in this patient was 11.11 GBq (Table 3).
(A) From left to right: axial, sagittal, and coronal SPECT/CT reconstruction of remaining thyroid tissue (arrows). (B) Activity concentration function in organ target.
Determination of small volumes is limited by the spatial resolution of the system. The spatial resolution at full width at half maximum was 13.6 mm, obtained by axial reconstruction of a point source of 131I. Figure 6 shows the result from the acquisition of a cylinder with a volume of 22 mL and 0.74 MBq of 131I with the described protocol. The apparent volume was 23.47 mL, with a difference of 6.3% from the actual volume. In Figure 6, the smallest volume of interest (VOI) represents the actual volume, and central VOI and biggest VOI are the apparent volumes measured with thresholds of 5% and 30%, respectively.
(A) Scattering-point function of SPECT of a cylinder of 22 mL filled with 131I. (B) Comparison of apparent and actual volume. kcnt = kilocount.
DISCUSSION
Preparation for dosimetry should be the same as for therapy to ensure reproducibility of 131I-NaI distribution (11). The patient must not have undergone imaging examinations with the use of iodinated contrast for a period of 6–8 wk (23). The patient’s metabolic status must be the same for dosimetry as for therapy, as metabolic status affects renal function and, thus, clearance rate and residence time (19,24).
The activity for dosimetry is small in comparison with the activity for therapy and must not be enough to alter the tumor’s ability to capture and retain iodine, called stunning. Studies show that even small activities can induce stunning (25). Activity should be limited to 4 Gy in the remaining thyroid tissue to avoid this effect. The 131I activity for the recommended diagnostic imaging is 10–20 MBq (19,26). The activity in this study was 74 MBq. Activity can be reduced to prevent stunning; however, it is necessary to reduce the image scanning speed so that the counting rate is not reduced, making quantification impossible.
When acquiring the 4 series of whole-body images, it is necessary to guarantee the same geometry in each series as in the previous series. The table elevation and detector distance must be maintained in each series. Patient positioning should be as identical as possible between series, and the patient’s whole body must be in the detector field of view (11). The automatic contouring systems of the equipment must be deactivated. Use of auxiliary straps to immobilize the arms close to the body is important to prevent undesirable movements.
Intervals between acquisitions must be consistent with the physical and biologic half-lives of iodine. The activity concentration in the image at 2 h is considered the maximum (100%) and is used as a reference for other measurements (6). Therefore, the patient should not urinate from the time of iodine administration until the end of this 2-h acquisition. From the samples assessed, significant radioactive material was found to be eliminated in the first hours. The mean activity concentration at 6 h was 78% ± 15%.
Tissue avid for 131I retained considerable iodine at 48 h, whereas the other tissues had almost completely eliminated the iodine. This difference provides contrast between these tissues, with better visualization of the structures. Acquisition at this interval allows assessment of pulmonary metastasis. The delayed image at 120 h contributed to adjustment of the accumulated activity curve. This image commonly shows accumulation of less than 2% of the initial activity. This interval can be adopted with 96-h imaging; however, if the accumulation is higher than 5%, 144-h imaging must be performed (11).
When there is diffuse pulmonary metastasis, the absorbed dose in the lung should be assessed. Pulmonary dosimetry plays an important role in preventing pulmonary fibrosis (19). On lung dosimetry studies, the 131I activity in the lung should be less than 2.96 GBq after 48 h. Higher activities can result in lung doses that exceed the limit for radiotoxicity effects (17–19). Thus, the image previously acquired within 48 h is used to calculate the maximum activity and maintain the dose limits in the lungs.
Because blood residence time is estimated through whole-body residence time, for which blood samples are not analyzed, it is necessary to consider the uncertainties in the calculations. Hänscheid et al. (13) proposed a conservative approach to estimating maximum activity. Blood residence time represents 14% ± 3% of body residence time (range, 8%–24%). Considering Equations 16 and 19 in cases in which blood residence time is greater than 14% of body residence time, the absorbed dose per activity can change considerably between the estimation and reality. Therefore, Hänscheid et al. propose a limit of 1.3 Gy, instead of 2 Gy, for absorbed dose in the marrow. In this way, even in cases of extreme variation between the real and measured values, the radiotoxicity limit in the hematopoietic system will not be exceeded. The data published by Willegaignon et al. (27,28) indicated that blood residence time was 10.3% ± 4% of body residence time (range, 2%–18%). In that work, if blood residence time had not been measured directly, adoption of a 1.3-Gy limit would have prevented dose limit extrapolation.
The half-life concept is applied to decay portrayed by an exponential function with a single term. Therefore, the time for decay of half the initial activity will not necessarily be the same as the second half-life, that is, a quarter of the initial activity. Compared with recent studies, there is agreement between the results. Barros, in 2019 (29), measured the dose rate of 98 hospitalized patients after a therapeutic dose of iodine for DTC therapy and found a mean effective half-life of 10.7 ± 4.5 h. For only the subgroup that was prepared with hormone suspension—that is, not using recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone—the mean was 12.5 ± 5 h. Barros also reported that patients older than 65 y had a mean effective half-life of 13.3 ± 4.7 h, approximately 30% higher than in middle-aged patients (10.3 ± 4.6 h).
The influence of spatial resolution on image quantification error is described as the partial-volume effect. As the size of a structure decreases, the measured concentration is reduced and the apparent volume is increased relative to the actual value (30). Organ-based dosimetry estimates the tumor-absorbed dose by targeting, to calculate the 131I activity to reach therapeutic levels. Organ dosimetry depends on tissue volume. For DTC, this process becomes even more challenging because the tissue is a remnant or, in some cases, micrometastases (20).
Cervical uptake examinations and whole-body research before therapy with low doses of radioiodine are provided for in the “Clinical Protocol and Therapeutic Guidelines for Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma,” approved by the Brazilian Ministry of Health (31). The objectives were to estimate the volume of remaining tissue or metastatic disease and the iodine avidity of these tissues. However, the ordinance concludes that patients considered at low and intermediate risk because of a low potential for distant metastasis may not need to undergo whole-body imaging. This measure also aims to prevent the stunning effect, which may harm the therapy.
CONCLUSION
Internal dosimetry takes into account physiologic characteristics in an individualized way, patient by patient, providing important data on 131I absorption and retention. The dosimetric techniques in this study could determine the maximum 131I activity to administer, considering the limits of radiotoxicity to the bone marrow and lungs as described in the literature. In severe cases of DTC, in which patients are classified as being at high risk, the organ-based dosimetry approach enables assessment of larger administered activities allowing elimination of the disease with a single dose. The dosimetric technique methodology was described in detail, allowing the reproduction of therapy planning as an individualized approach.
DISCLOSURE
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
KEY POINTS
QUESTION: What is the application of internal dosimetry in the care of patients undergoing radioiodine therapy for differentiated thyroid carcinoma?
PERTINENT FINDINGS: Through different techniques, a wide variation of retention time for 131I was obtained. The median dose absorbed by the bone marrow was 0.117 mGy/MBq and median whole-body residence time was 22.0 h, with an effective half-life of 15.6 h.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PATIENT CARE: Internal dosimetry provides information relevant to safe dose limits for application to DTC radioiodine therapy, especially in advanced cases of the disease for which the use of greater activities may be necessary.
Footnotes
Published online Jun. 14, 2022.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication November 30, 2021.
- Accepted for publication June 8, 2022.