RATIONALE/INTRODUCTION
Differentiation between amyloid light-chain (AL) and amyloid transthyretin (ATTR) cardiac amyloidosis is critical because of the differences in treatment. AL cardiac amyloidosis is treated with chemotherapy or stem-cell transplantation. ATTR cardiac amyloidosis is treated with disease-modifying agents that silence, stabilize, or disrupt ATTR protein misfolding and by the management of heart failure symptoms. ATTR cardiac amyloidosis demonstrates avid uptake of 99mTc-pyrophosphate in the myocardium, whereas AL cardiac amyloid has minimal or no avidity. Although the binding mechanism of 99mTc-pyrophosphate is unknown, it is believed to bind in microcalcifications in amyloid fibrils. ATTR, compared with AL, amyloidosis has a higher density of microcalcifications related to the chronicity of the disease.
INDICATIONS
Differentiation of ATTR from AL cardiac amyloidosis.
Evaluation of patients with heart failure and an increased left ventricular wall thickness not due to other reasons.
Evaluation of African-American patients more than 60 y old with heart failure and an increased left ventricular wall thickness greater than 12 mm not due to other reasons.
Evaluation of patients more than 60 y old with unexplained heart failure and preserved ejection fraction.
Evaluation of patients, particularly older men, with signs of heart failure in the presence of unexplained neuropathy, bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome, or atrial arrhythmias without typical risk factors.
Evaluation of patients with a known or suspected family history of amyloidosis.
Assessment for ATTR cardiac amyloidosis in patients with cardiac MRI or echocardiography findings consistent with cardiac amyloidosis.
Evaluation of suspected ATTR cardiac amyloidosis in patients with contraindications to cardiac MRI, such as those with implantable devices or renal insufficiency.
CONTRAINDICATIONS/TECHNICAL CONSTRAINTS
Pregnancy/breastfeeding (pregnancy must be excluded according to local institutional policy; if the patient is breastfeeding, appropriate radiation safety instructions should be provided).
A recent nuclear medicine study (radiopharmaceutical-dependent).
PATIENT PREPARATION/EDUCATION
There are no specific patient preparation requirements. The patient may eat and take medications as necessary before the study.
A focused history containing the following elements should be obtained:
○ Past medical history: heart failure, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (particularly in men), right heart failure (e.g., hepatomegaly, ascites, or lower extremity edema), unexplained atrial arrhythmias or conduction system disease, a pacemaker, concentric left ventricular wall thickening, hypertension that resolved over time, intolerance to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or β-blockers, bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome, lumbar spinal stenosis, previous orthopedic procedures, biceps tendon rupture, unexplained peripheral neuropathy, autonomic dysfunction (e.g., postural hypotension or alternating bowel pattern).
○ Family history of amyloidosis, cardiomyopathy, or polyneuropathy.
○ Signs and symptoms including shortness of breath during exercise or when lying down; swelling of the feet, ankles, and legs; dizziness, weakness, fatigue, irregular heartbeat, numbness or tingling in the hands or feet; skin thickening, easy bruising, enlarged tongue, diarrhea, constipation, frequent urination or incontinence.
○ Current medications.
○ Results of clinical laboratory tests, including serum κ/λ-free light chain ratio (abnormal if the ratio is <0.26 or >1.65), serum protein immunofixation (abnormal if monoclonal protein is detected), urine protein immunofixation (abnormal if monoclonal protein is detected), troponin levels and N-terminal pro–brain natriuretic peptide.
○ Results of other diagnostic tests, including echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and electrocardiography.
RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL IDENTITY, DOSE, AND ROUTE OF ADMINISTRATION
The radiopharmaceutical identity, dose, and route of administration are described in Table 1.
Radiopharmaceutical Identity, Dose, and Route of Administration
99mTc-pyrophosphate is primarily used for cardiac amyloidosis imaging in the United States. 99mTc-3,3-diphosphono-1,2-propanodicarboxylic acid (DPD) is used in Europe but is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the United States. 99mTc-hydroxymethylenediphosphonate (HMDP) can also be used for cardiac amyloidosis imaging. It is approved for use in the United States and may be substituted in times of 99mTc-pyrophosphate shortage. However, access to 99mTc-HMDP may be limited. Although no studies to date have directly compared the 3 tracers, published literature suggests they can be used interchangeably. When 99mTc-DPD and 99mTc-HMDP are used, whole-body scintigraphy in addition to planar and SPECT imaging is suggested to demonstrate other soft-tissue uptake.
99mTc-methylene diphosphonate, although widely available in the United States, has a lower sensitivity and should not be used for cardiac amyloid imaging.
ACQUISITION PARAMETERS: DYNAMIC/STATIC/PLANAR
The acquisition parameters are described in Table 2.
99mTc-Pyrophosphate Cardiac Amyloidosis Imaging Parameters
ACQUISITION INSTRUCTIONS
After injection of the 99mTc-pyrophosphate, planar imaging is performed after a 3-h delay to allow blood pool clearance.
For planar imaging, the patient is placed supine with the arms above the head. For large-field-of-view cameras, the patient’s shoulders are positioned near the top of the field of view to visualize the entire ribcage. Anterior and left lateral images are acquired for 750,000 counts.
For SPECT imaging using a dual-head camera, the detectors are configured at 90° for a minimum of 32 stops at 25 s/stop. Absence of motion is verified before the patient is allowed to leave the facility.
COMMON OPTIONS
In times of 99mTc-pyrophosphate shortage in the United States, 99mTc-HMDP may be substituted for 99mTc-pyrophosphate. When 99mTc-HMDP is used, whole-body imaging (10–14 cm/min) in addition to planar and SPECT imaging is suggested to demonstrate extracardiac soft-tissue uptake (gluteal, shoulder, chest, and abdominal walls).
PROCESSING INSTRUCTIONS
The anterior planar image is used to create a circular region of interest over the heart. Care must be taken to avoid including any extraneous activity outside the heart, such as in the sternum, the lung, or a hot rib due to previous injury.
The heart region is mirrored (same size) by placing a second circular region on the opposite side of the chest on the flat area of the ribs (contralateral lung region), again ensuring there is no extraneous activity such as in the sternum, the spine, or a rib injury.
The ratio of the heart to the contralateral lung is calculated by dividing the heart region by the contralateral lung region. A ratio of 1.3 or more is positive for cardiac amyloidosis.
The SPECT data are reconstructed using filtered backprojection or iterative reconstruction and displayed in the coronal, sagittal, and transverse projections.
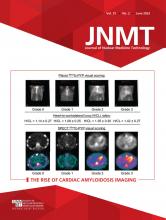
The planar and SPECT images are visually assessed and assigned a grade of 0–3 based on myocardial uptake compared with rib uptake (Table 3). Grades 2 and 3 are considered abnormal.
SPECT Semiquantitative Visual Scoring
PRECAUTIONS
Interpretation of 99mTc-pyrophosphate imaging and diagnosis of ATTR cardiac amyloidosis cannot be based on the planar and SPECT results alone. AL systemic amyloidosis must be excluded by serum and urine immunofixation and a serum-free AL assay in all patients with positive scan results.