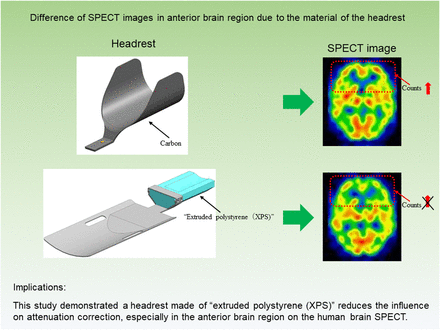
Visual Abstract
Abstract
Previous reports suggest that a headrest made of carbon significantly influences cerebral blood flow in the anterior and posterior regions by image reconstruction and attenuation correction (AC). The present study aimed to develop a headrest that reduces the influence of the AC process on human brain SPECT. Methods: To validate the performance of a headrest made of extruded polystyrene (XPS), 10 healthy controls and 43 patients with cerebrovascular disease underwent 99mTc-ethyl cysteinate dimer SPECT using a carbon headrest and an XPS headrest. We evaluated the anterior-to-posterior and middle-to-posterior ratio of the brain regions in filtered backprojection (FBP) Chang AC, ordered-subset expectation maximization (OSEM) Chang AC, and OSEM CT-based AC. Results: The anterior-to-posterior ratio was significantly higher with the carbon headrest than with the XPS headrest in FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC (P < 0.001). There was no significant difference between the materials in OSEM CT-based AC. The middle-to-posterior ratio did not differ to a statistically significant extent in any correction process. Conclusion: Acquisition of brain SPECT images with an XPS headrest and processing by the FBP or OSEM Chang AC method enables the influence of the headrest to be reduced, especially in anterior and posterior brain regions.
In the acquisition of brain SPECT images, various interactions (e.g., image reconstruction, attenuation correction [AC], and scatter correction [SC]) should be considered. The influence of these interactions results in decreased image contrast and errors for which AC and SC compensate. There are 2 representative methods for AC in SPECT: Chang AC and CT-based AC (CTAC). Chang AC is based on the assumption of uniform attenuation of γ-rays by intracranial tissues. However, since there are complex structures in the cranium (e.g., air, soft tissues, the paranasal sinus, and various degrees of skull thickness), attenuation is difficult to accurately correct (1). On the other hand, the recent widespread use of SPECT/CT has led to correction using CT data, such as CTAC. Attenuation of intracranial tissue that is nonuniform with the attenuation coefficient distribution derived from CT data can also be corrected. Thus, CTAC is expected to become more accurate than Chang AC (2).
A headrest is indispensable for brain SPECT. At present, carbon and polyethylene are the materials commonly used to construct standard headrests. Since the CT value of carbon is 300 Hounsfield units (HU), which affects the degree of γ-ray attenuation, γ-ray attenuation can affect image reconstruction processes, including AC and SC. Previous reports that compared SPECT images constructed using 2 types of AC methods have shown that CTAC is more accurate than the Chang method based on experimental data obtained with a phantom simulating the brain (3). Furthermore, in the Chang method, the anterior region of the brain shows relatively high blood flow because uniform correction is performed without considering the attenuation of γ-rays in part of the headrest. Thus, CTAC may contribute to reducing the influence of the headrest in comparison to Chang AC. However, Chang AC is still used in the reconstruction process for SPECT because SPECT/CT is not widespread enough. Therefore, headrest materials with a low CT value are needed because of the rareness of SPECT/CT systems.
We previously investigated the influence of headrests on brain SPECT using various SC and AC methods (4). We acquired a SPECT image with and without a carbon headrest to compare SPECT images. The blood flow value in the anterior region of the brain was higher than that evaluated by methods other than ordered-subset expectation maximization (OSEM) and CTAC image reconstruction. Thus, SPECT images are affected by the headrest unless both OSEM and CTAC are used to process the image. To solve this problem, we thought it necessary to use a headrest with a low CT value, almost equivalent to air, rather than carbon. Finally, we found a material, extruded polystyrene (XPS), that has a low CT value (practically equivalent to air), and we developed a new headrest made of this material. The purpose of this study was to compare the XPS headrest with a carbon headrest in healthy controls and patients with cerebrovascular disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of Yamagata University Faculty of Medicine for epidemiologic research (approval 2018-199). The participants gave written informed consent to inclusion in the study and publication of their data.
Subjects
Healthy Controls
We enrolled 10 healthy controls (male, n = 10; mean age, 50.20 ± 7.97 y; range, 32–59 y) who had no organic lesions on MRI and no stenosis or occlusion of the intracranial artery on MR angiography. The fact that the healthy control group comprised only men was coincidental; no selection bias was made. They were assessed by brain 99mTc-ethyl cysteinate dimer (ECD) SPECT with headrests made of carbon and XPS from July 2018 to April 2019.
Patients with Cerebrovascular Disease
We enrolled 43 patients (male, n = 30; female, n = 13; mean age, 59.46 ± 16.46 y; range, 22–85 y). Seventeen patients had cervical internal carotid artery stenosis, 16 had moyamoya disease, and 4 had intracranial artery stenosis. They were assessed by brain 99mTc-ECD SPECT with carbon and XPS headrests from October 2018 to August 2020.
SPECT Acquisition
Images were acquired by 99mTc-ECD SPECT/CT using a Symbia T2 (Siemens Healthineers) with a rotating, dual-detector γ-camera; a low-energy high-resolution collimator; and 360° continuous rotation (2.5 min/rotation × 6 rotations). Magnification was 1.45, the matrix was 128 × 128 (3.3 mm/pixel), the main window was 141 ± 10.5 keV, and the subwindow was 7%. The subjects were intravenously injected with 600 MBq of 99mTc-ECD while supine with their eyes closed and their head placed on the headrest. The SPECT acquisition with the carbon headrest took 20 min, starting 5 min after injection. The SPECT acquisition with the XPS headrest then took 20 min, starting 30 min after injection. CT imaging was also performed for both.
Headrests
The existing headrest (Fig. 1A) was of carbon, covered the occipital to the temporal regions, and had a CT value of 300 HU.
(A) Carbon headrest covering temporal to occipital regions of head, with CT value of 300 HU. (B) Hybrid headrest constructed from XPS and stainless steel, covering occipital region of head (which is in contact with XPS), with CT value of −980 HU.
The new headrest (Fig. 1B) was a hybrid of XPS and stainless steel (SUS304). XPS was chosen because it is easy to process, high in strength, low in cost, not metal, and as low as −980 HU in CT value. It was structured without temporal parts to reduce the attenuation of γ-rays. To increase stability of the head, we formed a dent in the headrest where it touches the back of the patient’s head. Testing of whether the headrest is strong enough for an actual clinical SPECT examination found that it could withstand a force of up to 200 N (kg⋅m/s2) and was as durable as the carbon headrest, which could withstand a force of up to 180 N. Furthermore, if the occipital region is close to stainless steel, the cerebral blood flow cannot be evaluated correctly because of metal artifacts. Therefore, the patient’s neck was positioned at the joint between the XPS and the stainless steel so that the stainless steel did not enter the cerebral blood flow evaluation site.
Image Analysis
Images were reconstructed by filtered backprojection (FBP) and ordered-subset expectation maximization (OSEM) with the combination of AC and SC. Chang AC, which is used in FBP and OSEM, creates an attenuation coefficient distribution that does not consider the headrest, as correction applies only to intracranial tissue. The CTAC used in OSEM creates an attenuation coefficient distribution of CT data and corrects both the intracranial tissue and the headrest. SC in SPECT was performed with a multienergy window.
99mTc-ECD SPECT was analyzed using a 3-dimensional (3D) stereotactic region-of-interest template (PDRadiopharma Inc.) to verify the influence of the headrest materials. The regions of interest were grouped into 12 segments in each hemisphere (A, callosomarginal; B, precentral; C, central; D, parietal; E, angular; F, temporal; G, posterior; H, pericallosal; I, lenticular nucleus; J, thalamus; K, hippocampus; and L, cerebellar) (5). We evaluated the count ratios for the anterior region (A+B) to the posterior region (G) and for the middle region (D+F) to the posterior region (G) to investigate the influence in the anterior and middle areas of the brain defined by the 3D stereotactic region-of-interest template (Fig. 2). We divided the images into the following 3 groups based on the methods of image reconstruction and AC: FBP Chang AC, OSEM Chang AC, and OSEM CTAC. The results for the 4 groups were compared between the carbon and XPS headrests.
3D stereotactic region-of-interest template for A+B/G ratio (A) and D+F/G ratio (B).
All statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS software program (version 26; SPSS Inc.). Differences in the A+B/G and D+F/G ratios among the different image reconstruction and correction methods with and without a headrest were analyzed using a paired t test. P values of less than 0.01 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
RESULTS
Healthy Controls
Table 1 compares the average A+B/G ratio and D+F/G ratio for each group using the carbon and XPS headrests. In FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC, there were significant differences in the A+B/G ratio between the carbon and XPS headrests (P < 0.001). On the other hand, in OSEM CTAC, there were no significant differences in the A+B/G ratio between the carbon and XPS headrests. There were no significant differences in the D+F/G ratio between the carbon and XPS headrests in any group.
Comparison of A+B/G and D+F/G Ratios Between Carbon and XPS Headrests in Healthy Controls (n = 10)
Figure 3 shows representative images. For the anterior brain region, images constructed using FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC with a carbon headrest showed a higher blood flow than those with an XPS headrest. On the other hand, images constructed using OSEM CTAC with a carbon headrest did not differ from images constructed using the same methods with an XPS headrest.
Comparison of 99mTc-ECD SPECT images obtained using carbon and XPS headrests in healthy controls. Images constructed with FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC using carbon headrest show higher cerebral blood flow in anterior part of brain than do images constructed with same methods using XPS headrest. In images constructed with OSEM CTAC, anterior and posterior parts of brain do not differ between images obtained using carbon and XPS headrests. SRT = stereotaxic region-of-interest template; ROI = region of interest.
Table 2 compares the average A+ B/G ratio and D+F/G ratio for each group between the carbon and XPS headrests. In FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC, significant differences in the A+B/G ratio were observed between the carbon and XPS headrests (P < 0.001). On the other hand, in OSEM CTAC, the A+B/G ratio did not differ between the carbon and XPS headrests. The D+F/G ratio did not differ to a statistically significant extent between the carbon and XPS headrests in any group.
Comparison of A+B/G and D+F/G Ratios Between Carbon and XPS Headrests in Patients with Cerebrovascular Disease (n = 43)
Figure 4 shows representative images. A 45-y-old man with atherothrombotic infarction due to left middle cerebral artery stenosis underwent MRI, 3D CT angiography, and 99mTc-ECD SPECT. MRI fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery sequences showed high-intensity lesions due to cerebral infarction in the left frontal and temporal lobes, including the insular cortex. 3D CT angiography showed severe stenosis of the left middle cerebral artery. For the anterior brain region, images constructed using FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC with a carbon headrest showed a higher blood flow than those obtained using an XPS headrest. On the other hand, images using OSEM CTAC with a carbon headrest did not differ from those obtained using an XPS headrest. The ratio of the ischemic side to the nonischemic side for the counts in region-of-interest B, which includes the middle cerebral artery territory, was 0.97 for carbon and 0.95 for XPS when viewed with FBP Chang AC.
Comparison of 99mTc-ECD SPECT images obtained using carbon and XPS headrests in patients with cerebrovascular disease. Fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery MR images show high-intensity lesions due to cerebral infarction in left frontal and temporal lobes, including insular cortex. 3D CT angiography shows severe stenosis of left middle cerebral artery. For anterior brain region, images constructed using FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC with carbon headrest show higher cerebral blood flow than do images constructed using same methods with XPS headrest. Images constructed using OSEM CTAC with carbon headrest show no difference from images constructed using same methods with XPS headrest. CTA = CT angiography; FLAIR = fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery; ROI = region of interest; SRT = stereotaxic region-of-interest template.
DISCUSSION
XPS as a Headrest Material
Previous studies reported that the headrest affected SPECT images when the Chang method was used for AC (2,3). The cause is considered to be the effect of the carbon from which the headrest is constructed on image reconstruction processes, especially AC. Since carbon has a high CT value of 300 HU, a carbon headrest can attenuate γ-rays generated from brain parenchyma adjacent to the headrest (e.g., the occipital region in Chang AC). Thus, the posterior region is relatively low, and the anterior region is considered to have a high cerebral blood flow distribution. Our previous report (4) showed that with FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC, significant differences in A+B/G ratio were observed between images obtained with and without a headrest. As a result, the anterior region appeared to have a higher cerebral blood flow than the posterior region, except when the OSEM CTAC method was used. Therefore, we need to create a headrest made of materials with low CT values and a low degree of γ-ray attenuation. Among such materials, the CT value of XPS is −980 HU, which is extremely low. Since XPS comprises innumerable bubbles, attenuation of γ-rays is considered to be small and the CT value low. Furthermore, the structure of XPS differs from that of expanded polystyrene beads, a well-known material with a structure consisting of continuous large bubbles. Since the bubbles are not continuous and are partitioned by a thin film of polystyrene resin in XPS, XPS has high strength and is suitable for headrest construction. Additionally, since XPS is in a completely sealed state, it suppresses water attenuation and heat conduction, is unlikely to change, and has high durability. Thus, we finally selected XPS as the headrest material.
Comparison Between Carbon and XPS for the Acquisition of 99mTc-ECD SPECT Images
For the anterior brain region, images obtained using FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC with a carbon headrest showed a higher blood flow than those with XPS in all participants. This is because the γ-rays generated from the brain parenchyma around the headrest, especially in the occipital region, are absorbed by the carbon headrest because of the γ-ray attenuation. Thus, the cerebral blood flow distribution is low in the occipital region and relatively high in the anterior region (3).
Our results show that use of an XPS headrest reduces the difference between the anterior and posterior regions of the brain. Thus, AC using XPS is less likely to affect image acquisition, even with the Chang method. In OSEM CTAC, there was no significant difference between carbon and XPS because correction from the CT data is based on both the intracranial tissue and the headrest, considering the nonuniformity of the brain in the CTAC method (6). Therefore, OSEM CTAC can be considered a reference standard. The A+B/G ratio by Chang AC using XPS and OSEM CTAC was similar. The skull has different degrees of thickness depending on the site. Since occipital bone is thicker than frontal bone, attenuation of γ-rays is considered to be more significant in the occipital region. Thus, the Chang method, which assumes that the head is a uniform absorber, is considered to be more significantly affected by the carbon headrest (7).
Regarding the clinical meaning of the difference between carbon and XPS, a representative case demonstrated in Figure 4 suggests the possibility that decreased blood flow will be underestimated in ischemic lesions when carbon is used for the headrest.
On the other hand, regarding the D+F/G ratio, no significant difference was observed between carbon and XPS in any combination of image reconstruction and AC methods. Regions D, F, and G were covered by the carbon headrest. Thus, like the posterior region, these regions were considered to be affected by the headrest.
A limitation of the present study is that, to minimize interactions such as attenuation and scattering of γ-rays emitted from brain tissue, the XPS headrest does not cover the side of the head, unlike the carbon headrest. Consequently, fixation during examination may have been a little unstable. Thus, further improvement is needed. In AC using the Chang method, the effect on images is considered to be less with the XPS headrest than with the conventional carbon headrest. Therefore, in the future, consideration may be given to use of XPS as a headrest material for SPECT image acquisitions.
CONCLUSION
We developed a new headrest constructed from XPS instead of carbon for brain SPECT. XPS has a low CT value of −980 HU, with excellent versatility, workability, and strength. The A+B/G ratio in FBP Chang AC and OSEM Chang AC significantly differed between the carbon and XPS headrests in healthy controls and patients with cerebrovascular disease. On the other hand, the A+B/G ratios in OSEM CTAC were not affected by the headrest material. There was no significant difference in the D+F/G ratio in FBP Chang AC or OSEM Chang AC. Thus, a headrest made of XPS reduces the influence of AC on brain SPECT images, especially in anterior and posterior brain regions when processed using the FBP or OSEM Chang AC method.
DISCLOSURE
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
KEY POINTS
QUESTION: Can a headrest be developed that reduces the influence of AC on SPECT images of the human brain?
PERTINENT FINDINGS: In healthy volunteers and cerebrovascular patients, a headrest made of XPS reduced the influence of AC on brain SPECT images, especially in anterior and posterior brain regions, when processed by the FBP or OSEM Chang AC method.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PATIENT CARE: The headrest made of XPS might allow acquisition of more precise human brain SPECT images.
Footnotes
Published online Nov. 9, 2022.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication July 28, 2022.
- Revision received November 3, 2022.