Abstract
Hepatopulmonary syndrome is characterized by intrapulmonary vascular dilatation causing hypoxemia in patients with liver disease. 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin (99mTc-MAA) scintigraphy has diagnostic value in suspected hepatopulmonary syndrome by detecting a clinically significant right-to-left shunt. In the presence of cirrhosis, 99mTc-MAA scanning with extrapulmonary organ visualization is specific for intrapulmonary shunting. 99mTc-MAA scintigraphy also provides the added value of quantification of the shunt.
We report a case of hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) confirmed by 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin (99mTc-MAA) scintigraphy. HPS is an uncommon condition in which there is hypoxemia due to intrapulmonary vascular dilatation in the context of liver disease.
CASE REPORT
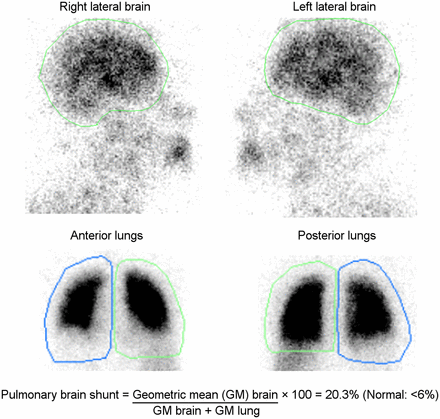
A 38-y-old man presented with dyspnea on exertion and thrombocytopenia. The patient was extensively evaluated, including MRI and liver biopsy, which demonstrated cirrhosis. The patient had a consistently low partial pressure of oxygen (≈55 mm Hg). The alveolar arterial oxygen gradient was 25 mm Hg. A transthoracic echocardiogram with saline showed microbubbles in the left heart chambers 4 cardiac cycles after contrast appearance in the right heart, suggestive of an extracardiac shunt—likely pulmonary arteriovenous malformation. 99mTc-MAA lung scintigraphy after injection of 144.3 MBq (3.9 mCi) of radiotracer showed increased tracer uptake in the brain, kidneys, spleen, and subcutaneous tissues, indicating a right-to-left shunt—likely an intrapulmonary shunt in the setting of cirrhosis (Fig. 1). On quantification, the brain shunt fraction was 20.3% (Fig. 2). An elevated alveolar–arterial gradient with a partial pressure of oxygen of less than 60, echocardiographic and scintigraphic evidence of intrapulmonary shunting, and no known chronic lung disease in the setting of cirrhosis were consistent with HPS in our patient. The patient is currently undergoing evaluation for a liver transplant.
99mTc-MAA planar whole-body image in anterior and posterior projections show intense radiotracer uptake in lungs (thin transverse arrows) and shunted activity in brain (oblique arrows), spleen (thick transverse arrows), kidneys (vertical arrows), and subcutaneous tissues (arrowheads).
Planar images of brain in right and left lateral projections and of lungs in anterior and posterior projections show areas of interest drawn to calculate lung–brain shunt.
DISCUSSION
The pathognomonic intrapulmonary vascular dilatations in HPS cause impaired oxygen transfer from alveoli to red blood cells, inducing an intrapulmonary right-to-left shunt. In HPS, hypoxemia and dyspnea may increase in the upright position because of preferential perfusion of dilated vessels in the lung bases (1). The severity of HPS based on the degree of hypoxemia is described as mild, moderate, severe, and very severe if PaO2 is 80 or more, 60–79, 50–59, and less than 50 mm Hg, respectively. HPS is frequently underdiagnosed (2). Currently, the only effective treatment for HPS is liver transplantation. It is important to diagnose HPS as early as possible to expedite treatment for a better outcome. Hypoxemia can be distinguished from HPS and other etiologies through bubble echocardiography, with arrival of bubbles in the left heart at least 3 cardiac cycles after contrast appearance in the right heart, or through 99mTc-MAA scintigraphy showing uptake in the brain (3). 99mTc-MAA scintigraphy is more specific than echocardiography and also can quantify and measure the degree of the shunt. Under good quality control measures and absence of a shunt, no extrapulmonary organs should be visualized, as the injected 99mTc-MAA particles are trapped in the pulmonary microvasculature. However, when there is an intrapulmonary shunt, a fraction of the particles enters the systemic circulation, leading to visualization of other organs and systems. The standard technique of calculating the percentage of lung–brain shunting is done by drawing regions of interest around the brain and lungs and determining the geometric mean of the brain and lung counts (4,5). HPS is suggested if the alveolar arterial oxygen gradient is at least 15 mm Hg or at least 20 mm Hg for patients more than 64 y old and the pulmonary brain shunt quantitative index for 99mTc-MAA is at least 6%. A whole-body 99mTc-MAA uptake calculation is another method for detecting intrapulmonary vascular dilatation (6).
CONCLUSION
Patients with a history of chronic liver disease along with dyspnea should be further evaluated for possible HPS. In patients with an elevated alveolar arterial gradient, bubble echocardiography or 99mTc scintigraphy aids in diagnosis of an intrapulmonary shunt. Though echocardiography is sensitive, it lacks specificity by providing false-positive results in patients with concomitant lung diseases. A positive 99mTc-MAA scan with tracer uptake in extrapulmonary organs in a cirrhotic patient is specific for HPS. 99mTc-MAA scintigraphy also quantifies the extent of a shunt.
DISCLOSURE
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Footnotes
Published online May. 24, 2022.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication March 28, 2022.
- Revision received April 27, 2022.