Abstract
Our objective was to harmonize multicenter 89Zr PET imaging for oncology trials and to evaluate lesion detection. Methods: Seven PET scanners were evaluated using a custom chest oncology phantom with 9 spheric lesions 7–20 mm in diameter. A 4:1 signal-to-background ratio simulated a patient dose of 92.5 MBq. Various image reconstructions were evaluated. Images were assessed for lesion detection, and recovery coefficients and background signal variance were measured. Results: Two scanners failed to provide acceptable images and data. Optimal reconstruction algorithms enabling adequate lesion detection and reliable quantification across the other 5 scanners were determined without compromising the data quality. On average, 95% of the 10-mm lesions were detected, and the 7-mm lesion was visualized by only 1 scanner. Background variance was 8.6%–16%. Conclusion: We established multicenter harmonization procedures for 89Zr PET imaging in oncology, optimizing small-lesion (≥10 mm) detectability and accurate quantification.
PET imaging of radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies can support the development of cancer immunotherapeutics by providing whole-body biodistribution and kinetic information on normal tissue and cancer lesions. PET scanner validation studies by organizations such as the American College of Radiology Imaging Network and EANM Research Ltd. use only technical phantoms with relatively high signal-to-background ratios (SBRs) and with high counts, as they are generally performed with 18F. Thus, they cannot be directly applied for scanner qualification for 89Zr imaging. 89Zr (78.4-h half-life) enables imaging of monoclonal antibodies over the biologically relevant period of several days (1–3). Multicenter imaging settings can accelerate implementation of clinical trials provided that scanners of different makes, models, and technologies are suitably qualified and that standardized imaging procedures are established to ensure that imaging data are qualitatively and quantitatively comparable across sites. Harmonization procedures for 18F-labeled tracers are relatively well established (4,5). However, 89Zr remains challenging because of its much lower count statistics (22.3% positron abundance), its nonprompt 909-keV γ-rays, and the low patient doses typically administered.
Furthermore, the high repeatability coefficients, varying up to 42% in lesions, estimated from clinical 89Zr PET studies (6) further substantiate the need for multisite imaging harmonization. Soderlund et al. (7) demonstrated good-quality images with longer-lived PET radionuclides than 18F but did not optimize image acquisition for doses likely to be used in clinical studies (37–92.5 MBq). Makris et al. (8) and Kaalep et al. (9) addressed the need for 89Zr imaging multicenter harmonization using National Electrical Manufacturers Association body phantoms but with a relatively high 10:1 SBR. These 3 studies, however, failed to evaluate image suitability for interpretation and lesion detection.
Here, we evaluated scanner and reconstruction performance using a chest oncology simulator phantom with 89Zr at clinically relevant doses and a 4:1 SBR. The optimal image reconstruction for each scanner was selected on the basis of small-lesion detection and quantitative performance.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
89Zr phantom imaging was performed with 7 PET scanners at 3 centers: DST, 600, 690, and 710 (GE Healthcare), and EXACT HR+, Biograph 6, and mCT (Siemens). A custom anthropomorphic oncology phantom representing a human chest with uniform body compartment and lung regions was used (Fig. 1). The phantom contained 9 fillable spheric lesions connected in series via small-bore tubing (1 × 7 mm, 5 × 10 mm, 2 × 15 mm, and 1 × 20 mm) (10,11). The phantom was filled to represent a 63-kg patient injected with 92.5 MBq of 89Zr. The body compartment was filled with approximately 1.46 kBq of 89Zr per milliliter. Some of this activity partially filled the lungs. The lesions were filled to create a 4:1 lesion SBR. The radioactive solutions were freshly prepared from approximately 37 MBq (1 mCi) of 89Zr supplied in 5 mL of 1 M oxalic acid, giving final oxalic acid concentrations of approximately 0.6 mM in the lesions and approximately 0.15 mM in the background. Three bed positions were acquired at 10 min per position as might be done clinically. Attenuation correction was performed using low-energy CT or a transmission scan in the HR+ scanner. Various reconstructions were performed on each scanner, using 2–4 iterations, 14–24 subsets, and 4- to 7-mm gaussian filters, as vendor software would allow. Reconstructed images were evaluated by both visual and quantitative methods. Image analysis was performed using OsiriX MD software (Pixmeo SARL).
Anthropomorphic chest oncology simulator with 9 internal spheric lesions. Lesion locations and size are shown at left. Phantom positioned supine in scanner is shown at right.
Visual Image Analysis
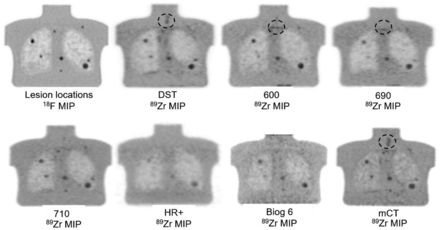
All image sets were reviewed, and one image set from each scanner was selected for analysis by an experienced operator. This selected image set had the least noise, and unequivocal visualization of at least four 10-mm and larger lesions, and was deemed suitable for radiologist review and reliable interpretation if used clinically. For a given scanner, this reconstruction set allowing the identification of the greatest number of lesions was selected. Although an 18F phantom image and the CT scan were used to verify lesion locations, spheric volumes of interest were delineated only on visually identified lesions. Figure 2 displays the thick-slice maximum-intensity-projection 18F reference images on a 710 scanner, showing the position of all lesions except the 7-mm lesion, which was visible only on the thin-slice images.
18F reference and 89Zr maximum-intensity-projection images. The 7-mm lesion was seen only on 710 thin-slice images (not shown). Circles show areas with focal 89Zr uptake not related to lesions.
Quantitative Image Analysis
Quantitative analysis was performed on the sets selected from each scanner in the visual assessment step. A background volume of interest approximately 25 mm in diameter was assigned in a uniform right shoulder area. The average SUV in the background volume of interest (SUVmean) and the SD were recorded and the percentage variation coefficient was calculated (100 × SD/SUVmean) and used as a measure of noise in the selected background region. In lesion volumes of interest, the SUVmax and the average SUV within a 1 cm3 spheric volume (SUVpeak) were used to create recovery coefficient (RC) curves. RC was defined as the ratio of activity concentration measured in the images to the activity concentration injected in the spheres. The measurements in the 10- and 15-mm lesions in the mediastinal region with a 4:1 SBR were used in the RC curves.
RESULTS
Visual Analysis
CT images were used to verify that lesions were uniformly filled, without bubbles. Some PET images showed minor focal 89Zr uptake on an inside phantom surface (Fig. 2), but its location away from lesions did not interfere with the visual and quantitative analysis. This focal uptake was not present during preliminary tests or in previously unused phantoms. It is unclear if this uptake was potentially mediated by biofilm contamination or could have been avoided with additional stabilizing agents (e.g., ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid).
All reconstructed image sets were visually reviewed, and the best image set for each scanner was selected and used for quantitative analysis. The selected reconstruction set parameters for these 5 scanners are given in Table 1.
Optimal Reconstruction Parameters for 89Zr Oncology Imaging
Table 2 shows the lesions visualized per scanner. The 20-mm lesion was visualized by all scanners, the 15- and 10-mm lesions were detected in 6 scanners and 5 scanners, respectively, and the 7-mm lesion was detected in the 710 scanner only. Visual review revealed that the Biograph 6 and HR+ images had the poorest noise characteristics: none of the 10-mm lesions were visualized, and the larger lesions were blurred, with low SBR. Figure 2 shows the thick-slice 710 18F reference and 89Zr maximum-intensity-projection images from all scanners. All lesions are included in these thick-slice maximum-intensity-projection images.
Lesion Visualization
Quantitative Analysis
The background-noise percentage-variation coefficients were 12.1% for the DST, 15.9% for the 600, 15.8% for the 690, 13.1% for the 710, 20.4% for the HR+, 36.4% for the Biograph 6, and 8.6% for the mCT. The SUVpeak RC curves were smoother than the SUVmax curves; therefore, only the SUVpeak curves were used for scanner harmonization and included in the results. The SUVpeak RC percentage decrease between 20-mm and 10-mm lesions calculated as 100% (SUVpeak 20 mm/SUVpeak 10 mm – 1) is shown in Figure 3. The largest decreases were observed for the Biograph 6 and HR+ scanners, at 99.7% and 120.3%, respectively, whereas the drop for all other scanners was less than 74%.
Percentage reduction of SUVpeak between 20- and 10-mm lesions.
Correlation of Visual and Quantitative Results
The Biograph 6 and HR+ scanners failed to perform adequately either visually or quantitatively; therefore, they were excluded from further analysis. Considering the low count density of the 89Zr images, the SUVpeak RC curves for the 5 remaining scanners showed reasonable agreement (Fig. 4). These scanners—DST, 600, 690, 710, and mCT—had similar quantitative performance and visual characteristics for noise and small-lesion detection. Lesion visualization performance was 100% for 20-mm lesions, 100% for 15-mm lesions, and 95% for 10-mm lesions. The 7-mm lesion was clearly visualized only with the 710 scanner.
SUVpeak RC curves for 5 harmonized scanners.
DISCUSSION
Several papers have investigated the limitations and accuracy of low-count PET imaging. Kadrmas and Christian (12) showed that reconstruction methods have a significant impact on lesion detection and, thus, that scanning duration and reconstruction algorithms need to be adapted to the imaging conditions. This was confirmed by Carlier et al. (13), who found that 90Y PET imaging in phantoms and patients resulted in image quality and quantitative measurements that varied with the reconstruction algorithms. Work by Makris et al. (8) and Kaalep et al. (9) addressed the need for 89Zr imaging multicenter harmonization using a uniform cylinder and National Electrical Manufacturers Association NU-2 phantoms. However, the large 10:1 SBR and very low background level used in these 2 studies may not be adequate to address the question of lesion visualization and quantification of less avid lesions likely to be observed during this type of study because of the persistent nature of monoclonal antibodies in most tissues.
We evaluated the 89Zr imaging performance of 7 PET scanners using an anthropomorphic phantom with a low radioactive dose and a 4:1 SBR. The recommended reconstruction methods enable optimal lesion detection and quantification. On the basis of the visual and quantitative analysis, the Biograph 6 and HR+ scanners had a poor performance in this low-count imaging situation. These scanners have hardware that is inherently less sensitive than scanners of more recent technology and are limited by their reconstruction algorithms.
Scanner validation and harmonization studies should be performed with the radionuclide being used in the clinical protocol, because the performance of scatter fraction modeling, half-life, randoms, and other factors may influence the reconstructed image quality and quantification.
CONCLUSION
We established a procedure for grading and harmonizing scanners and reconstruction parameters using a 89Zr-filled chest simulator phantom. Scanner-specific reconstruction parameters enabling comparable optimal performance and small-lesion (≥10 mm) detection were determined in 5 scanners to be used in clinical 89Zr-monoclonal antibody PET imaging studies.
DISCLOSURE
Paul E. Christian is a Genentech, Inc., consultant. Simon-Peter Williams, Alex de Crespigny, and Sandra Sanabria Bohorquez are Genentech, Inc., employees and own stock in Roche. Justin Albiani and Nicholas Sandella are Invicro LLC employees. All work was funded by Genentech Inc. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Acknowledgments
We thank Keith Bigham of Medical Designs, Inc., Newtown, CT, for manufacturing the custom phantoms.
Footnotes
Published online Oct. 11, 2019.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication April 30, 2019.
- Accepted for publication August 12, 2019.