Abstract
A case of previously unknown metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma presented as focal photopenia on hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scintigraphy. Differential diagnosis of focal photopenia and heterogenous hepatic radiotracer uptake on hepatobiliary scintigraphy is reviewed.
Colorectal adenocarcinoma is the third most common type of cancer worldwide, with approximately 1.36 million new cases diagnosed each year (1). Approximately 30%–50% of patients with colorectal cancer develop liver metastases (2). This report presents a case of metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma first discovered on a hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scan, which to our knowledge has not previously been described in the literature, and reviews the differential diagnosis of focal photopenia and heterogeneous hepatic radiotracer uptake on hepatobiliary scintigraphy.
CASE REPORT
A 50-y-old man with no significant past medical history presented to his primary care physician for 1 mo of worsening aching and burning in the right upper quadrant and suprapubic pain with associated dysuria, nausea, and weight loss. Urinalysis performed in the office revealed trace hematuria. The clinician hypothesized the pain to be related to separate etiologies: GERD versus cholelithiasis to explain the right upper quadrant pain and nephrolithiasis causing the suprapubic pain. Abdominal ultrasound and a hepatobiliary scan were ordered. In addition, the patient was prescribed famotidine and advised to drink more water.
Hepatobiliary scanning was performed, before ultrasound, with 198 MBq (5.35 mCi) of 99mTc-disofenin. Anterior and left-anterior-oblique images of the abdomen were obtained in the supine position at 45 and 50 min after radiotracer administration, respectively. At 60 min after radiotracer administration, the patient was injected with 2 μg of cholecystokinin infused over 60 min, during which a dynamic acquisition was performed to calculate gallbladder ejection fraction, which was normal.
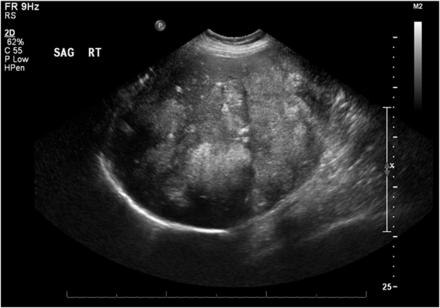
Images obtained at 45 and 50 min after 99mTc-disofenin administration demonstrated heterogeneous liver uptake with multiple scattered photopenic areas (Fig. 1). Given that these findings were suspected of being liver masses, abdominal ultrasound was recommended. Ultrasound showed multiple echogenic masses throughout the liver (Fig. 2). Subsequent laboratory tests yielded an elevated carcinoembryonic antigen level of 1,738 and a lactate dehydrogenase level of 804. Contrast-enhanced CT of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated hypodense masses throughout the liver, lymphadenopathy, and a primary sigmoid colon mass invading the bladder (Fig. 3). Core liver biopsy revealed metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma.
Anterior (A) and left anterior oblique (B) spot images obtained 45 and 50 min after 99mTc-disofenin administration show heterogeneous distribution of radiotracer activity throughout liver as well as large photopenic defect (arrow).
Sagittal ultrasound of right hepatic lobe shows numerous echogenic masses.
(A) Axial portal-vein–phase contrast-enhanced CT images of abdomen show hypodense masses scattered throughout liver. (B–D) Also seen is primary sigmoid colon mass (arrow, C) invading bladder (arrow, B) and lymphadenopathy (arrow, D).
DISCUSSION
In the normal liver, hepatocytes demonstrate uptake of iminodiacetic acid, leading to homogeneous radiotracer distribution. Theoretically, any process that replaces or displaces normal hepatocytes would be expected to cause focal photopenic areas or heterogenous hepatic radiotracer uptake. The potential causes are many but include benign hepatic cysts, metastasis, primary liver masses, and less common processes such as focal confluent hepatic fibrosis and Caroli disease (3). Focal hepatic fibrosis would demonstrate wedge-shaped areas of decreased radiotracer activity, whereas hepatic cysts and metastases are more likely to demonstrate randomly distributed photopenic defects. Caroli disease is known to initially show multiple focal photopenic defects that later fill with radiotracer on subsequent delayed imaging (3). In the setting of cirrhosis, a heterogeneous scintigraphic appearance of the liver can be seen because of the replacement of normally functioning hepatocytes with hepatocytes that exhibit either increased or decreased function, such as is seen with regenerative nodules or with the development of poorly differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma (4).
CONCLUSION
Focal photopenia on hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scanning is suggestive of metastatic or primary neoplasia. In addition to correlating the findings with patient history and prior imaging, one should consider further evaluation with other imaging modalities.
DISCLOSURE
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Footnotes
Published online Aug. 3, 2018.
- Received for publication April 30, 2018.
- Accepted for publication June 29, 2018.