Visual Abstract
Abstract
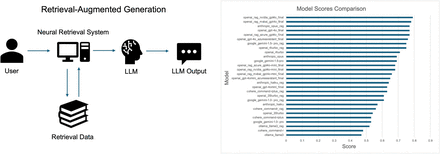
This study investigated the application of large language models (LLMs) with and without retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) in nuclear medicine, particularly their performance across various topics relevant to the field, to evaluate their potential use as reliable tools for professional education and clinical decision-making. Methods: We evaluated the performance of LLMs, including the OpenAI GPT-4o series, Google Gemini, Cohere, Anthropic, and Meta Llama3, across 15 nuclear medicine topics. The models’ accuracy was assessed using a set of 600 sample questions, covering a range of clinical and technical domains in nuclear medicine. Overall accuracy was measured by averaging performance across these topics. Additional performance comparisons were conducted across individual models. Results: OpenAI’s models, particularly openai_nvidia_gpt-4o_final and openai_mxbai_gpt-4o_final, demonstrated the highest overall accuracy, achieving scores of 0.787 and 0.783, respectively, when RAG was implemented. Anthropic Opus and Google Gemini 1.5 Pro followed closely, with competitive overall accuracy scores of 0.773 and 0.750 with RAG. Cohere and Llama3 models showed more variability in performance, with the Llama3 ollama_llama3 model (without RAG) achieving the lowest accuracy. Discrepancies were noted in question interpretation, particularly in complex clinical guidelines and imaging-based queries. Conclusion: LLMs show promising potential in nuclear medicine, improving diagnostic accuracy, especially in areas like radiation safety and skeletal system scintigraphy. This study also demonstrates that adding a RAG workflow can increase the accuracy of an off-the-shelf model. However, challenges persist in handling nuanced guidelines and visual data, emphasizing the need for further optimization in LLMs for medical applications.
- nuclear medicine
- AI models
- retrieval-augmented generation
- large language models
- diagnostic accuracy
- radiation safety
Footnotes
Published online May 9, 2025.
This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
SNMMI members
Login to the site using your SNMMI member credentials
Individuals
Login as an individual user