FIGURE 1.
FIGURE 1.
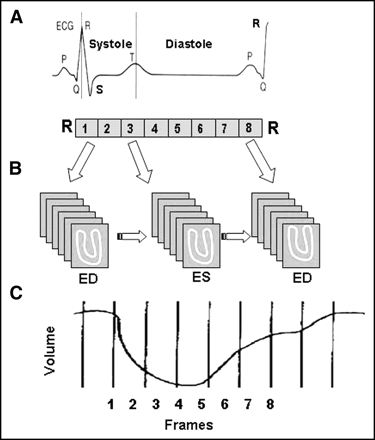
Principle of ECG-gated acquisition. R–R interval on ECG, representing 1 cardiac cycle, is typically divided into 8 frames of equal duration (A). Image data from each frame are acquired over multiple cardiac cycles and stored separately in specific locations (“bin”) of computer memory (B). When all data in a bin are added together, image represents a specific phase of cardiac cycle. Typically, a volume curve is obtained, which represents endocardial volume for each of 8 frames (C). ED = end-diastole; ES = end-systole.