Abstract
Objective
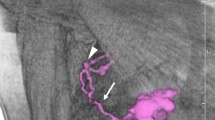
Lymphoscintigraphy is an effective method for detecting sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs). However, the rate and degree of SLN detection is not uniform. We quantified SLNs detected with lymphoscintigraphy, and investigated correlations with factors that may influence detection. We then attempted to predict SLN metastasis from lymph node counts, comparing the predictions to subsequent biopsy results.
Methods
We assessed lymph node counts in 100 breast cancer patients in whom a single SLN was detected with a fixed lymphoscintigraphy procedure. We examined correlations between the counts and factors known to influence lymphoscintigraphic SLN detection (age, body mass index, tumor size, and presence or absence of metastasis), and determined reference values (lymph node counts of 10.0, 19.4 and 53.0) which were used to predict SLN metastasis in 100 subsequent patients. The predictions were then compared with the SLN biopsy findings.
Results
SLN counts correlated strongly with the presence or absence of metastasis, with metastasis-positive lymph nodes showing significantly lower counts than negative nodes (p < 0.001). Prediction of SLN metastasis achieved a 100% positive predictive value at a reference value of 10.0, and a 100% negative predictive value at a reference value of 53.0. At a reference value of 19.4, the sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy were 77.8, 73.2, and 74.0%, respectively.
Conclusions
The SLN counts detected with lymphoscintigraphy were significantly lower in metastasis-positive lymph nodes than in metastasis-negative lymph nodes. This suggests that prediction of SLN metastasis in breast cancer is possible using lymphoscintigraphy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nemoto T, Vana J, Bedwani RN, Baker HW, McGregor FH, Murphy GP. Management and survival of female breast cancer: results of a national survey by the American College of Surgeons. Cancer. 1980;45:2917–24.
Krag DN, Weaver DL, Alex JC, Fairbank JT. Surgical resection and radiolocalization of the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer using a gamma probe. Surg Oncol. 1993;2:335–40.
Giuliano AE, Kirgan DM, Guenther JM, Morton D. Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy for breast cancer. Ann Surg. 1994;220:391–401.
Krag D, Weaver D, Ashikaga T, Moffat F, Klimberg VS, Shriver C, et al. The sentinel node in breast cancer: a multicenter validation study. New Engl J Med. 1998;339:941–6.
Motomura T, Inaji H, Komoike Y, Kasugai T, Nagumo S, Noguchi S, et al. Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients with clinically negative lymph-nodes. Breast Cancer. 1999;6:259–62.
Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Galimberti V, Viale G, Zurrida S, Bedoni M, et al. Sentinel-node biopsy to avoid axillary dissection in breast cancer with clinically negative lymph-nodes. Lancet. 1997;349:1864–7.
Noguchi M. Sentinel lymph node biopsy and breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2002;89:21–34.
Imoto S, Murakami K, Ikeda H, Fukukita H, Moriyama N. Mammary lymphoscintigraphy with various radiopharmaceuticals in breast cancer. Ann Nucl Med. 1999;13:325–9.
Yeung HW, Cody HS, Turlakow A, Riedel ER, Fey J, Gonen M, et al. Lymphoscintigraphy and sentinel node localization in breast cancer patients: a comparison between 1-day and 2-day protocols. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:420–3.
McMasters KM, Wong SL, Martin RAG, Chao C, Tuttle TM, Noyes RD, et al. Dermal injection of radioactive colloid is superior to peritumoral injection for breast cancer sentinel lymph node biopsy: results of a multi-institutional study. Ann Surg. 2001;233:676–87.
Kim R, Osaki A, Kojima J, Toga T. Significance of lymphoscintigraphic mapping with Tc-99m human serum albumin and tin colloid in sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2001;19:991–6.
Pelosi E, Bello M, Giors M, Ala A, Giani R, Bussone R, et al. Sentinel lymph node detection in patients with early-stage breast cancer: comparison of periareolar and subdermal/peritumoral injection techniques. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:220–5.
Cox CE, Pendas S, Cox JM, Joseph E, Shons AR, Yeatman T, et al. Guidelines for sentinel node biopsy and lymphatic mapping of patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg. 1998;227:645–53.
Haigh PI, Hansen NM, Giuliano AE, Edwards GK, Ye W, Glass EC. Factors affecting sentinel node localization during preoperative breast lymphoscintigraphy. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:1682–8.
Cox CE, Dupont E, Whitehead GF, Ebert MD, Nguyen K, Peltz ES, et al. Age and body mass index may increase the chance of failure in sentinel lymph node biopsy for women with breast cancer. Breast J. 2002;8:88–91.
Wang L, Yu J, Wang Y, Zuo W, Gao Y, Fan J, et al. Preoperative lymphoscintigraphy predicts the successful identification but is not necessary in sentinel lymph nodes biopsy in breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:2215–20.
Nakashima K, Kurebayashi J, Sonoo H, Tanaka K, Ikeda M, Shiiki S, et al. Preoperative dynamic lymphoscintigraphy predicts sentinel lymph node metastasis in patients with early breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2010;17(1):17–21. doi:10.1007/s12282-009-0123-y.
Martin RCG, Edwards MJ, Wong SL, Tuttle TM, Carlson DJ, Brown CM, et al. Practical guidelines for optimal gamma probe detection of sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer: results of a multi-institutional study. Surgery. 2000;128:139–44.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Teruhiko Takayama for supervising our study for many years. We also express our gratitude to Dr. Hideo Inaji, Dr. Yoshifumi Komoike, and Dr. Masato Ishitobi of the Department of Surgery for their cooperation in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noguchi, A., Onoguchi, M., Ohnishi, T. et al. Predicting sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer with lymphoscintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med 25, 221–226 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-010-0459-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-010-0459-6