Abstract
Objective
It is controversial whether alteration of cerebral perfusion plays an important role in the pathophysiology of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) and can help to predict the outcome after shunt surgery.
Materials and Methods
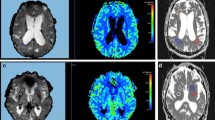
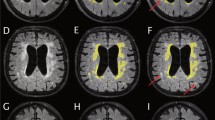
28 patients with suspected NPH were examined clinically (Homburg Hydrocephalus Scale, walking test, incontinence protocol) and by 3D dynamic susceptibility based perfusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging (PWI–MRI) before and after cerebrospinal fluid release (spinal tap test, STT). The perfusion parameters (negative integral (NI), time of arrival (T0), time to peak (TTP), mean transit time, and the difference TTP—T0 were analysed.
Results
Three different groups of patients were identified preoperatively: In group 1 seven patients showed an increase in the cerebral perfusion and a clinical improvement after STT. The second group (9 patients) also revealed an increase of the cerebral perfusion, but no significant alteration of the clinical assessment could be found. In the third group neither the cerebral perfusion nor the clinical assessment changed. 14 of the 16 patients (group 1 and 2) were examined three months after shunt placement. 11 patients showed a good or excellent result, 2 patients revealed a fair assessment, and only 1 patient had transiently improved. No patient was downgraded after shunting. In the patient group 1 and 2 the NI increased significantly (effect size: 34%), whereas in group 3 no significant alteration of NI was observed.
Conclusion
PWI–MRI improves the prediction of outcome after shunt placement in patients with NPH and can offer new insights into the pathophysiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RD, Fischer CM, Hakim S, Ojeman RG, Sweet WH (1965) Symptomatic Occult Hydrocephalus With Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure. N Engl J Med 273:117–126
Hebb AO, Cusimano MD (2001) Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: a Systematic Review of Diagnosis and Outcome. Neurosurgery 49(5):1166–1184
Savoiardo M, Grisoli M (2001) Imaging Dementias. Eur Radiol 11(3):484–492
Boon AJ, Tans JT, Delwel EJ, Egeler– Peerdeman SM, Hanlo PW, Wurzer HA, Hermans J (2000) The Dutch Normal– Pressure Hydrocephalus Study. How to Select Patients for Shunting? An Analysis of Four Diagnostic Criteria. Surg Neurol 53(3):201–207
Wikkelso C, Andersson H, Blomstrand C, Lindqvist G, Svendsen P (1986) Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Predictive Value of the Cerebrospinal Fluid Tap–Test. Acta Neurol Scand 73(6):566–573
Meier U (2001) The Importance of the Intrathecal Infusion Test in the Diagnostics of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Biomed Tech (Berl) 46(7–8):191–199
Raftopoulos C, Chaskis C, Delecluse F, Cantraine F, Bidaut L, Brotchi J (1992) Morphological Quantitative Analysis of Intracranial Pressure Waves in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurol Res 14(5):389–396
Kiefer M, Steudel WI (1994) Moderne Diagnostik und Therapie des hydrocephalus beim älteren Patienten. Saarländisches Ärzteblatt 10:498–504
Owler BK, Pickard JD (2001) Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus and Cerebral Blood Flow: a Review. Acta Neurol Scand 104(6):325–342
Greitz T (1969) Effect of Brain Distension on Cerebral Circulation. Lancet 1(7600):863–865
Waldemar G, Schmidt JF, Delecluse F, Andersen AR, Gjerris F, Paulson OB (1993) High Resolution SPECT With [99mTc]–d,l–HMPAO in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Before and After Shunt Operation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56(6):655–664
Hertel F, Walter C, Schmitt M, Morsdorf M, Jammers W, Busch HP, Bettag M (2003) Is a Combination of Tc– SPECT or Perfusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Spinal Tap Test Helpful in the Diagnosis of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74(4):479–484
Black PM, Ojemann RG, Tzouras A (1985) CSF Shunts for Dementia, Incontinence, and Gait Disturbance. Clin Neurosurg 32:632–651
Flacke S, Urbach H, Folkers PJ, Keller E, van den Brink JS, Traber F, Block W, Gieseke J, Schild HH (2000) Ultra–Fast Three–Dimensional MR Perfusion Imaging of the Entire Brain in Acute Stroke Assessment. J Magn Reson Imaging 11(3):250–259
Bortz J, Lienert GA, Boehnke K (2000) Verteilungsfreie Methoden in der Biostatistik. 2nd ed. Berlin, Springer Verlag
Kirk RE (1982) Experimental design. Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd edition. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates
Mamo HL, Meric PC, Ponsin JC, Rey AC, Luft AG, Seylaz JA (1987) Cerebral Blood Flow in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Stroke 18(6):1074–1080
Meyer JS, Tachibana H, Hardenberg JP, Dowell RE Jr, Kitagawa Y, Mortel KF (1984) Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Influences on Cerebral Hemodynamic and Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure–Chemical Autoregulation. Surg Neurol 21(2):195–203
Mori K, Maeda M, Asegawa S, Iwata J (2002) Quantitative Local Cerebral Blood Flow Change After Cerebrospinal Fluid Removal in Patients With Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Measured by a Double Injection Method With N–Isopropyl–p–[123I] Iodoamphetamine. Acta Neurochir. (Wien. ) 144(3):255–262
Kristensen B, Malm J, Fagerland M, Hietala SO, Johansson B, Ekstedt J, Karlsson T (1996) Regional Cerebral Blood Flow, White Matter Abnormalities, and Cerebrospinal Fluid Hydrodynamics in Patients With Idiopathic Adult Hydrocephalus Syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 60(3):282–288
Kushner M, Younkin D, Weinberger J, Hurtig H, Goldberg H, Reivich M (1984) Cerebral Hemodynamics in the Diagnosis of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurology 34(1):96–99
Lee SK, Kim DI, Jeong EK, Yoon PH, Cha SH, Lee JH (2002) Temporal Changes in Reversible Cerebral Ischemia on Perfusion– and Diffusion– Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging: the Value of Relative Cerebral Blood Volume Maps. Neuroradiology 44(2):103–108
Klinge P, Fischer J, Brinker T, Heissler HE, Burchert W, Berding G, Knapp WH, Samii M (1998) PET and CBF Studies of Chronic Hydrocephalus: a Contribution to Surgical Indication and Prognosis. J Neuroimaging 8(4):205–209
Tanaka A, Kimura M, Nakayama Y, Yoshinaga S, Tomonaga M (1997) Cerebral Blood Flow and Autoregulation in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 40(6):1161–1165
Ostergaard L, Sorensen AG, Kwong KK, Weisskoff RM, Gyldensted C, Rosen BR (1996) High Resolution Measurement of Cerebral Blood Flow Using Intravascular Tracer Bolus Passages. Part II: Experimental Comparison and Preliminary Results. Magn Reson Med 36(5):726–736
Wittsack HJ, Ritzl A, Modder U (2002) User Friendly Analysis of MR Investigations of the Cerebral Perfusion: Windows(R)–Based Image Processing. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 174(6):742–746
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walter, C., Hertel, F., Naumann, E. et al. Alteration of cerebral perfusion in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus measured by 3D perfusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol 252, 1465–1471 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0891-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0891-z