Abstract
Purpose
The clinical introduction of 68Ga-PSMA-11 (“HBED-CC”) ligand targeting the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) has been regarded as a significant step forward in the diagnosis of prostate cancer (PCa). In this study, we provide human dosimetry and data on optimal timing of PET imaging after injection.
Methods
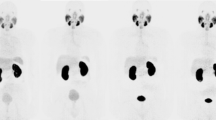
Four patients with recurrent PCa were referred for 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT. Whole-body PET/CTlow-dose scans were conducted at 5 min, and 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 h after injection of 152–198 MBq 68Ga-PSMA-11. Organs of moderate to high uptake were used as source organs; their total activity was determined at all measured time points. Time–activity curves were created for each source organ as well as for the remainder. The radiation exposure of a 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET was identified using the OLINDA-EXM software. In addition, tracer uptake was measured in 16 sites of metastases.
Results
The highest tracer uptake was observed in the kidneys, liver, upper large intestine, and the urinary bladder. Mean organ doses were: kidneys 0.262 ± 0.098 mGy/MBq, liver 0.031 ± 0.004 mGy/MBq, upper large intestine 0.054 ± 0.041 mGy/MBq, urinary bladder 0.13 ± 0.059 mGy/MBq. The calculated mean effective dose was 0.023 ± 0.004 mSv/MBq (=0.085 ± 0.015 rem/mCi). Most tumor lesions (n = 16) were visible at 3 h p.i., while at all other time points many were not qualitatively present (10/16 visible at 1 h p.i.).
Conclusions
The mean effective dose of a 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET is 0.023 mSv/MBq. A 3-h delay after injection was optimal timing for 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in this patient cohort.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29.
Schmid DT, John H, Zweifel R, Cservenyak T, Westera G, Goerres GW, et al. Fluorocholine PET/CT in patients with prostate cancer: initial experience. Radiology. 2005;235:623–8.
Igerc I, Kohlfurst S, Gallowitsch HJ, Matschnig S, Kresnik E, Gomez-Segovia I, et al. The value of 18F-choline PET/CT in patients with elevated PSA-level and negative prostate needle biopsy for localisation of prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35:976–83.
Kwee SA, DeGrado T. Prostate biopsy guided by 18F-fluorocholine PET in men with persistently elevated PSA levels. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35:1567–9. author reply 1570.
Hacker A, Jeschke S, Leeb K, Prammer K, Ziegerhofer J, Sega W, et al. Detection of pelvic lymph node metastases in patients with clinically localized prostate cancer: comparison of [18F]fluorocholine positron emission tomography-computerized tomography and laparoscopic radioisotope guided sentinel lymph node dissection. J Urol. 2006;176:2014-8-9.
Sweat SD, Pacelli A, Murphy GP, Bostwick DG. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression is greatest in prostate adenocarcinoma and lymph node metastases. Urology. 1998;52:637–40.
Mannweiler S, Amersdorfer P, Trajanoski S, Terrett JA, King D, Mehes G. Heterogeneity of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) expression in prostate carcinoma with distant metastasis. Pathol Oncol Res. 2009;15:167–72.
Hillier SM, Maresca KP, Femia FJ, Marquis JC, Foss CA, Nguyen N, et al. Preclinical evaluation of novel glutamate-urea-lysine analogues that target prostate-specific membrane antigen as molecular imaging pharmaceuticals for prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69:6932–40.
Maresca KP, Hillier SM, Femia FJ, Keith D, Barone C, Joyal JL, et al. A series of halogenated heterodimeric inhibitors of prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) as radiolabeled probes for targeting prostate cancer. J Med Chem. 2009;52:347–57.
Cho SY, Gage KL, Mease RC, Senthamizhchelvan S, Holt DP, Jeffrey-Kwanisai A, et al. Biodistribution, tumor detection, and radiation dosimetry of 18F-DCFBC, a low-molecular-weight inhibitor of prostate-specific membrane antigen, in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med. 2012;53:1883–91.
Barrett JA, Coleman RE, Goldsmith SJ, Vallabhajosula S, Petry NA, Cho S, et al. First-in-man evaluation of 2 high-affinity PSMA-avid small molecules for imaging prostate cancer. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med. 2013;54:380–7.
Tagawa ST, Milowsky MI, Morris M, Vallabhajosula S, Christos P, Akhtar NH, et al. Phase II study of Lutetium-177-labeled anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen monoclonal antibody J591 for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2013;19:5182–91.
Hillier SM, Maresca KP, Lu G, Merkin RD, Marquis JC, Zimmerman CN, et al. 99mTc-labeled small-molecule inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen for molecular imaging of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med. 2013;54:1369–76.
Banerjee SR, Pullambhatla M, Foss CA, Nimmagadda S, Ferdani R, Anderson CJ, et al. 64Cu-labeled inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen for PET imaging of prostate cancer. J Med Chem. 2014;57:2657–69.
Szabo Z, Mena E, Rowe SP, Plyku D, Nidal R, Eisenberger MA, et al. Initial evaluation of [(18)F]DCFPyL for prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted PET imaging of prostate cancer. Mol Imaging Biol MIB Off Publ Acad Mol Imaging. 2015;17:565–74.
Schäfer M, Bauder-Wüst U, Leotta K, Zoller F, Mier W, Haberkorn U, et al. A dimerized urea-based inhibitor of the prostate-specific membrane antigen for 68Ga-PET imaging of prostate cancer. EJNMMI Res. 2012;2:23.
Eder M, Schäfer M, Bauder-Wüst U, Hull W-E, Wängler C, Mier W, et al. 68Ga-complex lipophilicity and the targeting property of a urea-based PSMA inhibitor for PET imaging. Bioconjug Chem. 2012;23:688–97.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Haberkorn U, Eder M, Eisenhut M, Zechmann CM. [68Ga]Gallium-labelled PSMA ligand as superior PET tracer for the diagnosis of prostate cancer: comparison with 18F-FECH. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39:1085–6.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Malcher A, Eder M, Eisenhut M, Linhart HG, Hadaschik BA, et al. PET imaging with a [68Ga]gallium-labelled PSMA ligand for the diagnosis of prostate cancer: biodistribution in humans and first evaluation of tumour lesions. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:486–95.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Zechmann CM, Malcher A, Eder M, Eisenhut M, Linhart HG, et al. Comparison of PET imaging with a (68)Ga-labelled PSMA ligand and (18)F-choline-based PET/CT for the diagnosis of recurrent prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:11–20.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Avtzi E, Giesel FL, Holland-Letz T, Linhart HG, Eder M, et al. The diagnostic value of PET/CT imaging with the (68)Ga-labelled PSMA ligand HBED-CC in the diagnosis of recurrent prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:197–209.
Eiber M, Maurer T, Souvatzoglou M, Beer AJ, Ruffani A, Haller B, et al. Evaluation of hybrid 68Ga-PSMA ligand PET/CT in 248 patients with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med. 2015;56:668–74.
Eder M, Neels O, Müller M, Bauder-Wüst U, Remde Y, Schäfer M, et al. Novel preclinical and radiopharmaceutical aspects of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-HBED-CC: a new PET tracer for imaging of prostate cancer. Pharm Basel Switz. 2014;7:779–96.
Reza Ay M, Zaidi H. Computed tomography-based attenuation correction in neurological positron emission tomography: evaluation of the effect of the X-ray tube voltage on quantitative analysis. Nucl Med Commun. 2006;27:339–46.
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E. OLINDA/EXM: the second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:1023–7.
1990 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Ann ICRP. 1991;21:1–201.
Krohn T, Verburg FA, Pufe T, Neuhuber W, Vogg A, Heinzel A, et al. [Ga]PSMA-HBED uptake mimicking lymph node metastasis in coeliac ganglia: an important pitfall in clinical practice. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging [Internet]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Citation&list_uids=25248644.
Herrmann K, Bluemel C, Weineisen M, Schottelius M, Wester H-J, Czernin J, et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry for a probe targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen for imaging and therapy. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med. 2015;56:855–61.
Zechmann CM, Afshar-Oromieh A, Armor T, Stubbs JB, Mier W, Hadaschik B, et al. Radiation dosimetry and first therapy results with a (124)I/ (131)I-labeled small molecule (MIP-1095) targeting PSMA for prostate cancer therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:1280–92.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Hetzheim H, Kratochwil C, Benesova M, Eder M, Neels OC, et al. The Theranostic PSMA ligand PSMA-617 in the diagnosis of prostate cancer by PET/CT: biodistribution in humans, radiation dosimetry, and first evaluation of tumor lesions. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med. 2015;56:1697–705.
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to the Klaus Tschira Foundation (grant no. 00.198.2012) for funding our research. In addition, we would like to thank our staff, in particular Stephanie Biedenstein, Kirsten Kunze, Larissa Engel, and Peter Seybold for their help in performing this analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the Klaus Tschira Foundation (grant no. 00.198.2012).
Conflict of interest
Ali Afshar-Oromieh has received honoraria from Siemens Healthcare for one educational talk. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All patients published in this manuscript signed a written informed consent form for the purpose of anonymized evaluation and publication of their data. All reported investigations were conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration and with our national regulations (German Medicinal Products Act, AMG §13 2b). This evaluation was approved by the ethics committee of the University of Heidelberg (S-321-2012).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
SUVs of the background at different times in all four patients. (GIF 78 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afshar-Oromieh, A., Hetzheim, H., Kübler, W. et al. Radiation dosimetry of 68Ga-PSMA-11 (HBED-CC) and preliminary evaluation of optimal imaging timing. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43, 1611–1620 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3419-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3419-0