Abstract
Purpose
Visual reading of [123I]IBZM SPECT scans depends on the experience of the interpreter. Therefore, semi-quantification of striatal IBZM uptake is commonly considered mandatory. However, semi-quantification is time consuming and prone to error, particularly if the volumes of interest (VOIs) are positioned manually. Therefore, the present paper proposes a new software tool (“IBZM tool”) for fully automated and standardised processing, evaluation and documentation of [123I]IBZM SPECT scans.
Methods
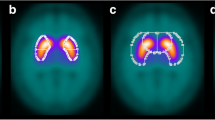
The IBZM tool is an easy-to-use SPM toolbox. It includes automated procedures for realignment and summation of multiple frames (motion correction), stereotactic normalisation, scaling, VOI analysis of striatum-to-reference ratio R, classification of R and standardised display. In order to evaluate the tool, which was developed at the University of Hamburg, the tool was transferred to the University of Hannover. There it was applied to 27 well-documented subjects: eight patients with multi-system atrophy (MSA), 12 patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) and seven controls. The IBZM tool was compared with manual VOI analysis.
Results
The sensitivity and specificity of the IBZM tool for the differentiation of the MSA subjects from the controls were 100% and 86%, respectively. The IBZM tool provided improved statistical power compared with manual VOI analysis.
Conclusion
The IBZM tool is an expert system for the detection of reduced striatal D2 availability on [123I]IBZM SPECT scans. The standardised documentation supports visual and semi-quantitative evaluation, and it is useful for presenting the findings to the referring physician. The IBZM tool has the potential for widespread use, since it appears to be fairly independent of the performance characteristics of the particular SPECT system used. The tool is available free of charge.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brucke T, Tsai YF, McLellan C, Singhanyom W, Kung HF, Cohen RM, et al. In vitro binding properties and autoradiographic imaging of 3-iodobenzamide ([125I]-IBZM): a potential imaging ligand for D-2 dopamine receptors in SPECT. Life Sci 1988;42:2097–2104
Costa DC, Verhoeff NP, Cullum ID, Ell PJ, Syed GM, Barrett J, et al. In vivo characterisation of 3-iodo-6-methoxybenzamide 123I in humans. Eur J Nucl Med 1990;16:813–816
Kung HF, Alavi A, Chang W, Kung MP, Keyes JW Jr, Velchik MG et al. In vivo SPECT imaging of CNS D-2 dopamine receptors: initial studies with iodine-123-IBZM in humans. J Nucl Med 1990;31:573–579
Tatsch K, Schwarz J, Oertel WH, Kirsch CM. SPECT imaging of dopamine D2 receptors with 123I-IBZM: initial experience in controls and patients with Parkinson’s syndrome and Wilson’s disease. Nucl Med Commun 1991;12:699–707
Schwarz J, Tatsch K, Arnold G, Gasser T, Trenkwalder C, Kirsch CM, et al. 123I-iodobenzamide-SPECT predicts dopaminergic responsiveness in patients with de novo parkinsonism. Neurology 1992;42:556–561
van Royen E, Verhoeff NF, Speelman JD, Wolters EC, Kuiper MA, Janssen AG. Multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy. Diminished striatal D2 dopamine receptor activity demonstrated by 123I-IBZM single photon emission computed tomography. Arch Neurol 1993;50:513–516
Plotkin M, Amthauer H, Klaffke S, Kuhn A, Ludemann L, Arnold G, et al. Combined 123I-FP-CIT and 123I-IBZM SPECT for the diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes: study on 72 patients. J Neural Transm 2005;112:677–692
Pilowsky LS, Costa DC, Ell PJ, Murray RM, Verhoeff NP, Kerwin RW. Clozapine, single photon emission tomography, and the D2 dopamine receptor blockade hypothesis of schizophrenia. Lancet 1992;340:199–202
Brucke T, Wober C, Podreka I, Wober-Bingol C, Asenbaum S, Aull S, et al. D2 receptor blockade by flunarizine and cinnarizine explains extrapyramidal side effects. A SPECT study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1995;15:513–518
Tauscher J, Kufferle B, Asenbaum S, Tauscher-Wisniewski S, Kasper S. Striatal dopamine-2 receptor occupancy as measured with [123I]iodobenzamide and SPECT predicted the occurrence of EPS in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics and haloperidol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2002;162:42–49
la Fougere C, Meisenzahl E, Schmitt G, Stauss J, Frodl T, Tatsch K et al. D2 receptor occupancy during high- and low-dose therapy with the atypical antipsychotic amisulpride: a 123I-iodobenzamide SPECT study. J Nucl Med 2005;46:1028–1033
Brucke T, Podreka I, Angelberger P, Wenger S, Topitz A, Kufferle B, et al. Dopamine D2 receptor imaging with SPECT: studies in different neuropsychiatric disorders. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1991;11:220–228
Oertel WH, Tatsch K, Schwarz J, Kraft E, Trenkwalder C, Scherer J, et al. Decrease of D2 receptors indicated by 123I-iodobenzamide single-photon emission computed tomography relates to neurological deficit in treated Wilson’s disease. Ann Neurol 1992;32:743–748
Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, van Dyck CH, Gil R, D’Souza CD, Erdos J, et al. Single photon emission computerized tomography imaging of amphetamine-induced dopamine release in drug-free schizophrenic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996;93:9235–9240
Booij J, Korn P, Linszen DH, van Royen EA. Assessment of endogenous dopamine release by methylphenidate challenge using iodine-123 iodobenzamide single-photon emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med 1997;24:674–677
Laruelle M, D’Souza CD, Baldwin RM, Abi-Dargham A, Kanes SJ, Fingado CL et al. Imaging D2 receptor occupancy by endogenous dopamine in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 1997;17:162–174
Guardia J, Catafau AM, Batlle F, Martin JC, Segura L, Gonzalvo B, et al. Striatal dopaminergic D2 receptor density measured by [123I]iodobenzamide SPECT in the prediction of treatment outcome of alcohol-dependent patients. Am J Psychiatry 2000;157:127–129
Verhoeff NP, Kapucu O, Sokole-Busemann E, van Royen EA, Janssen AG. Estimation of dopamine D2 receptor binding potential in the striatum with iodine-123-IBZM SPECT: technical and interobserver variability. J Nucl Med 1993;34:2076–2084
Hertel A, Weppner M, Baas H, Schreiner M, Maul FD, Baum RP, et al. Quantification of IBZM dopamine receptor SPET in de novo Parkinson patients before and during therapy. Nucl Med Commun 1997;18:811–822
Tatsch K, Asenbaum S, Bartenstein P, Catafau A, Halldin C, Pilowsky LS, et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine procedure guidelines for brain neurotransmission SPET using 123I-labelled dopamine D2 receptor ligands. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:BP23–BP29
Radau PE, Linke R, Slomka PJ, Tatsch K. Optimization of automated quantification of 123I-IBZM uptake in the striatum applied to parkinsonism. J Nucl Med 2000;41:220–227
Popperl G, Radau P, Linke R, Hahn K, Tatsch K. Diagnostic performance of a 3-D automated quantification method of dopamine D2 receptor SPECT studies in the differential diagnosis of parkinsonism. Nucl Med Commun 2005;26:39–43
Verhoeff NP, Brucke T, Podreka I, Bobeldijk M, Angelberger P, Van Royen EA. Dynamic SPECT in two healthy volunteers to determine the optimal time for in vivo D2 dopamine receptor imaging with 123I-IBZM using the rotating gamma camera. Nucl Med Commun 1991;12:687–697
Gutzki J, Martin B, Wilke F, Buchert R, Mester J, Clausen M. Time dependence of striatum to background ratio in 123-I-IBZM SPET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:S157
Buchert R, Mester J, Bohuslavizki KH, Clausen M. Performance characteristics of a new low-cost four-headed small-field-of-view gamma camera dedicated for brain imaging. J Nucl Med 2001;42:886
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline JP, Frith CD, Frackowiak RSJ. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Hum Brain Mapp 1995;2:189–210
Larisch R, Meyer W, Klimke A, Kehren F, Vosberg H, Muller-Gartner HW. Left-right asymmetry of striatal dopamine D2 receptors. Nucl Med Commun 1998;19:781–787
Duarte P, Hustinx R, Couturier O, Smith RJ, Alavi A. Hottest pixel analysis: useful value or statistical artifact? J Nucl Med 1999;40:292P
Kuikka JT, Bergstrom KA, Ahonen A, Hiltunen J, Haukka J, Lansimies E, et al. Comparison of iodine-123 labelled 2 beta-carbomethoxy-3 beta-(4-iodophenyl)tropane and 2 beta-carbomethoxy-3 beta-(4-iodophenyl)-N-(3-fluoropropyl)nortropane for imaging of the dopamine transporter in the living human brain. Eur J Nucl Med 1995;22:356–360
Berding G, Gratz KF, Kolbe H, Meyer GJ, Dengler R, Knoop BO, et al. 123I-IBZM SPECT: reconstruction methodology and results in parkinsonism and dystonia. Nuklearmedizin 1994;33:194–199
Weissenborn K, Berding G, Kostler H. Altered striatal dopamine D2 receptor density and dopamine transport in a patient with hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2000;15:173–178
Muller-Vahl KR, Berding G, Kolbe H, Meyer GJ, Hundeshagen H, Dengler R, et al. Dopamine D2 receptor imaging in Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand 2000;101:165–171
Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S. Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 1999;56:33–39
Gilman S, Low PA, Quinn N, Albanese A, Ben-Shlomo Y, Fowler CJ, et al. Consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Sci 1999;163:94–98
Armitage P, Berry G. Statistical methods in medical research, 3rd edn. Malden, USA: Blackwell Science Ltd; 1998
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986;1:307–310
Acton PD, Pilowsky LS, Suckling J, Brammer MJ, Ell PJ. Registration of dynamic dopamine D2 receptor images using principal component analysis. Eur J Nucl Med 1997;24:1405–1412
Nikkinen P, Liewendahl K, Savolainen S, Launes J. Validation of quantitative brain dopamine D2 receptor imaging with a conventional single-head SPET camera. Eur J Nucl Med 1993;20:680–683
Meyer JH, Gunn RN, Myers R, Grasby PM. Assessment of spatial normalization of PET ligand images using ligand-specific templates. Neuroimage 1999;9:545–553
Gispert JD, Pascau J, Reig S, Martinez-Lazaro R, Molina V, Garcia-Barreno P, et al. Influence of the normalization template on the outcome of statistical parametric mapping of PET scans. Neuroimage 2003;19:601–612
Van Laere K, Koole M, D’Asseler Y, Versijpt J, Audenaert K, Dumont F, et al. Automated stereotactic standardization of brain SPECT receptor data using single-photon transmission images. J Nucl Med 2001;42:361–375
Laulumaa V, Kuikka JT, Soininen H, Bergstrom K, Lansimies E, Riekkinen P. Imaging of D2 dopamine receptors of patients with Parkinson’s disease using single photon emission computed tomography and iodobenzamide I 123. Arch Neurol 1993;50:509–512
Stamatakis EA, Glabus MF, Wyper DJ, Barnes A, Wilson JT. Validation of statistical parametric mapping (SPM) in assessing cerebral lesions: A simulation study. Neuroimage 1999;10:397–407
Jenkins TW, Truex RC. Dissection of the human brain as a method for its fractionation by weight. Anat Rec 1963;147:359–366
Acton PD, Pilowsky LS, Kung HF, Ell PJ. Automatic segmentation of dynamic neuroreceptor single-photon emission tomography images using fuzzy clustering. Eur J Nucl Med 1999;26:581–590
Plotkin M, Amthauer H, Quill S, Marzinzik F, Klostermann F, Klaffke S, et al. Imaging of dopamine transporters and D2 receptors in vascular parkinsonism: a report of four cases. J Neural Transm 2005;112:1355–1361
Parellada E, Lomena F, Catafau AM, Bernardo M, Font M, Fernandez-Egea E, et al. Lack of sex differences in striatal dopamine D2 receptor binding in drug-naive schizophrenic patients: an IBZM-SPECT study. Psychiatry Res 2004;130:79–84
Wenning GK, Donnemiller E, Granata R, Riccabona G, Poewe W. 123I-beta-CIT and 123I-IBZM-SPECT scanning in levodopa-naive Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 1998;13:438–445
Hwang WJ, Yao WJ, Wey SP, Shen LH, Ting G. Downregulation of striatal dopamine D2 receptors in advanced Parkinson’s disease contributes to the development of motor fluctuation. Eur Neurol 2002;47:113–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchert, R., Berding, G., Wilke, F. et al. IBZM tool: a fully automated expert system for the evaluation of IBZM SPECT studies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33, 1073–1083 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-006-0067-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-006-0067-9