Abstract
Purpose
To characterize ordered-subset expectation maximization algorithm with a fixed 3D Gauss post-reconstruction filtering (OSEM) in99mTc SPECT as for noise, contrast and spatial resolution with varying number of subset and iteration and to compare OSEM with an optimized set of parameters, with filtered backprojection (FBP) with filter parameters typical of brain and myocardial SPECT, both with and without Chang’s method of attenuation correction (AC).
Methods
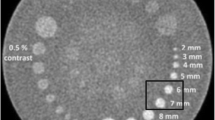
SPECT images of a Jaszczak phantom with cold rod inserts, hot and cold spheres and capillary line sources were acquired. Different background activity concentrations of the phantom were simulated as well as different lesion-to-background activity ratios. OSEM reconstructions were halted after 5, 10 and 15 iterations using 4, 8 and 16 subsets.
Results
The effect of subset and iteration number over noise is additive: thus, it is possible to define an EM-equivalent iteration number that indicates the product between the subset and the iteration numbers. Noise increases linearly with increasing EM-equivalent iteration number. For each level of nominal contrast, the measured contrast after OSEM shows a little increase with increasing iteration number and saturates after 80 EM-equivalent iterations. The application of AC leads to diminished contrast values both in FBP and OSEM. The contrast of cold lesions after OSEM increases with increasing number of EM-equivalent iteration number: after 80 iterations the contrast values with OSEM overtake the ones obtained with FBP; contrast values diminished as background concentration raised. Resolution values did not change with increasing EM-equivalent iteration number and were higher than those obtained with FBP.
Conclusion
The major findings of the present work are the demonstration of additivity of subset and iteration in OSEM over noise, with the possibility of defining an EM equivalent iteration number, and the superiority of OSEM with respect to FBP in terms of spatial resolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barret HH, Wilson DW, Tsui BMW. Noise properties of the EM algorithm: part I. Theory.Phys MedBiol 1994; 39:833- 846.
Liow J-S, Strother SC. Practical tradeoffs between noise, quantitation and number of iterations for maximum likelihood-based reconstruction.IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1991; 10: 563–571.
Miller TR, Wallis JW. Clinically important characteristics of maximum-likelihood reconstruction.J Nucl Med 1992; 33: 1678–1684.
Snyder DL, Miller MI, Thomas LJ Jr, Politte DG. Noise and edge artifacts in maximum likelihood reconstruction for emission tomography.IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1987; 6: 228–238.
Hudson HM, Larkin RS. Accelerated image reconstruction using ordered subsets of projection data.IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1994; 13: 601–609.
Yokoi T, Shinohara H, Onishi H. Performance evaluation of OSEM reconstruction algorithm incorporating three-dimensional distance-dependent resolution compensation for brain SPECT: a simulation study.Ann Nucl Med 2002; 16: 11–18.
Lau YH, Hutton BF, Beekman FJ. Choice of collimator for cardiac SPET when resolution compensation is included in iterative reconstruction.Eur J Nucl Med 2001; 28: 39–7.
Hutton BF, Baccarne V. Efficient scatter modelling for incorporation in maximum likelihood reconstruction.Eur J Nucl Med 1998; 25: 1658–1665.
Hutton BF, Lau YH. Application of distance-dependent resolution compensation and post-reconstruction filtering for myocardial SPECT.Phys Med Biol 43: 1679–1693.
Kamphuis C, Beekman FJ, van Rijk PP, Viergever MA. Dual matrix ordered subsets reconstruction for accelerated 3D scatter compensation in single-photon emission tomography.Eur J NuclMed 1998; 25: 8–18.
Lalush DS, Tsui BMW. Performance of ordered-subset reconstruction algorithms under conditions of extreme attenuation and truncation in myocardial SPECT.J Nucl Med 2000; 41: 737–744.
Blocklet D, Seret A, Popa N, Schoutens A. Maximum- likelihood reconstruction with ordered subsets in bone SPECT.J NuclMed 1999; 40: 1978–1984.
Case JA, Licho R, King MA, Weaver JP. Bone SPECT of the spine: a comparison of attenuation correction techniques.J Nucl Med 1999; 40: 604–613.
Kauppinen T, Koskinen MO, Alenius S, Vanninen E, Kuikka JT. Improvement of brain perfusion SPET using iterative reconstruction with scatter and non-uniform attenuation correction.Eur J Nucl Med 2000; 27: 1380–1386.
Vanhove C, Defrise M, Franken PR, Everaert H, Deconinck F, Bossuyt A. Interest of the ordered subsets expectation maximization (OS-EM) algorithm in pinhole single-photon emission tomography reconstruction: a phantom study.Eur J Nucl Med 2000; 27: 140–146.
Wells GR, King MA, Simkin PH, Judy PF, Brill AB, Gifford HC, et al. Comparing filtered backprojection and ordered subsets expectation maximization for small-lesions detection and localization in67Ga SPECT.J Nucl Med 2000; 41: 1391–1399.
Gonzalez RC, Wood RE.Digital Image Processing. Reading, MA; Addison Wesley Publishing, 1992: 208–209.
Iftikar I, Koutelou M, Mahmarian JJ, Verani MS. Simultaneous perfusion tomography and radionuclide angiography during dobutamine stress.J Nucl Med 1996; 37: 1306- 1310.
Kiat H, Maddhai J, Roy LT, et al. Comparison of technetium 99m methyl isobutyl isonitrile ant thallium 201 for evaluation of coronary artery disease by planar and tomographic methods.Am Heart J 1989; 117: 1–11.
Taillefer R, DePuey EG, Udelson JE, Bellar GA, Latour Y, Reeves F. Comparative diagnostic accuracy of Tl-201 and Tc-99m sestamibi SPECT imaging (perfusion and ECG- gated SPECT) in detecting coronary artery disease in women.J Am Coll Cardiol 1997; 29: 69–77.
Chang LT. A method for attenuation correction in radionuclide computed tomography.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1978; 25: 638–643.
Beekman FJ, Viergever MA. Evaluation of fully 3D iterative scatter compensation and post-reconstruction filtering in SPECT. In: Grangeat P, Amans J-L, eds.Three-dimensional image reconstruction in radiology and nuclear medicine. Dordrecht Boston London; Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1996: 163–175.
Pedroli G, Crespi A, De Agostini A, Farinelli C, Moretti R, et al. The quality control of SPET systems: results of an inter-laboratory comparison study in Italy.J Nucl Med and All Sci 1989; 33: 396–400.
Winer BJ. Statistical principles in experimental design. New York; McGraw-Hill, 1971.
Hutton BF, Hudson HM, Beekman FJ. A clinical perspective of accelerated statistical reconstruction.Eur J Nucl Med 1997; 24: 797–808.
Wallis JW, Miller TR. Rapidly converging iterative reconstruction algorithms in single-photon emission computed tomography.J Nucl Med 1993; 34: 1793–1800.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brambilla, M., Cannillo, B., Dominietto, M. et al. Characterization of ordered-subsets expectation maximization with 3d post-reconstruction gauss filtering and comparison with filtered backprojection in99mTc SPECT. Ann Nucl Med 19, 75–82 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027384
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027384