Abstract
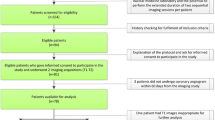
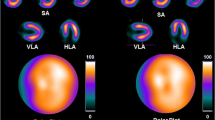
The purpose of this study was to compare the clinical utility of two image reconstruction algorithms in myocardial perfusion SPECT (single-photon emission computed tomography): filtered back-projection (FBP) and ordered subset expectation maximization (OSEM). A rest/stress one-day protocol with99mTc-MIBI or tetrofosmin was performed on 102 consecutive patients who underwent coronary angiography. After SPECT data acquisition, images were reconstructed with FBP and OSEM algorithms. We assessed diagnostic performance (sensitivity, specificity and accuracy) in detecting coronary artery stenosis and evaluated regional tracer uptake with a 4-point scoring system. Although there were no significant differences in diagnostic performance between FBP and OSEM reconstruction, the OSEM method yielded higher uptake in the RCA area than the FBP method by reducing the count-loss artifact due to hepatic uptake of the tracers. In addition, regional uptake in the LCX area was significantly lower in the OSEM image than in the FBP image; this phenomenon was observed mainly in patients with coronary stenosis and/or infarction in the LCX territory. In conclusion, OSEM and FBP offered comparable diagnostic performance in stress myocardial perfusion SPECT. The OSEM method contributed to reduction of the count-loss artifact in inferior and posterior walls and to easy recognition of hypoperfusion in the LCX area.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Lange K, Carson R. EM reconstruction algorithms for emission and transmission tomography.J Comput Assist Tomogr 1984; 8: 306–316.
Floyad CE Jr, Jaszczak RJ, Coleman RE. Convergence of the maximum likelihood reconstruction algorithm for emission computed tomography.Phys Med Biol 1987; 32: 463–476.
Reader AJ, Visvikis D, Erlandsson K, Ott RJ, Flower MA. Intercomparison of four reconstruction techniques for positron volume imaging with rotating planar detectors.Phys Med Biol 1998; 43: 823–834.
Hutton BF, Accarne BV. Efficient scatter modeling for incorporation in maximum likelihood reconstruction.Eur J Nucl Med 1998; 25: 1658–1665.
Hutton BF, Lau YH. Application of distance-dependent resolution compensation and post-reconstruction filtering for myocardial SPECT.Phys Med Biol 1998; 43: 1679–1693.
Lonneux M, Borbath I, Bol A, Coppens A, Sibomana M, Bausart R, et al. Attenuation correction in whole-body FDG oncological studies: the role of statistical reconstruction.Eur J Nucl Med 1999; 26: 591–598.
Blocklet D, Seret A, Popa N, Schoutens A. Maximum-likelihood reconstruction with ordered subsets in bone SPECT.J Nucl Med 1999; 40: 1978–1984.
Dey D, Slomka PJ, Hahn LJ, Kloiber R. Comparison of ordered subsets expectation maximization and Chang’s attenuation correction method in quantitative cardiac SPECT: a phantom study.Nucl Med Commun 1998; 19: 1149–1157.
Lonneux M, Borbath I, Bol A, Coppens A, Sibomana M, Bausart R, et al. Attenuation correction in whole-body FDG oncological studies: the role of statistical reconstruction.Eur J Nucl Med 1999; 26: 591–598.
Case JA, Licho R, King MA, Weaver JP. Bone SPECT of the spine: a comparison of attenuation correction techniques.J Nucl Med 1999; 40: 604–613.
Lalush DS, Tsui BMW. Performance of ordered-subset reconstruction algorithms under conditions of extreme attenuation and truncation in myocardial SPECT.J Nucl Med 2000; 41: 737–744.
Shepp L, Logan B. The Fourier reconstruction of a head section.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1974; 21: 21–43.
Germano G, Chua T, Kiat H, Areeda JS, Berman DS. A quantitative phantom analysis of artifacts due to hepatic activity in technetium-99m myocardial perfusion SPECT.J Nucl Med 1994; 35: 356–359.
King MA, Xia W, delVries DJ, Pan TS, Villegas BJ, Dahlberg S, et al. A Monte Carlo investigation of artifacts caused by liver uptake in single-photon emission computed tomography perfusion imaging with technetium 99m-labeled agents.J Nucl Cardiol 1996; 3: 18–29.
Matsunari I, Tanishima Y, Taki J, Ono K, Nishide H, Fujino S, et al. Early and delayed technetium-99m-tetrofosmin myocardial SPECT compared in normal volunteers.J Nucl Med 1996; 37: 1622–1626.
Nuyts J, Dupont P, Maegdenbergh VV, Vleugels S, Suetens P, Mortelmans L. A study of the liver-heart artifact in emission tomography.J Nucl Med 1995; 36: 133–139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, J., Hashimoto, J., Suzuki, T. et al. Comparison of image reconstruction algorithms in myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med 15, 79–83 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03012138
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03012138