Abstract
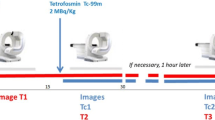
We have devised a new position (Monzen position) which can suppress the influence of scattered rays from surrounding organs (liver, etc.) when conducting myocardial imaging. Unlike the conventional techniques, which require a waiting period of 30-60 minutes before imaging can be started after the infusion of technetium-99m sestamibi or technetium-99m tetrofosmin, this position allows single-photon emission tomography to be started about 5-10 minutes after the infusion of the tracer. Therefore, with this technique the total time required for imaging is reduced and consequently the physical and mental burden of the patient is also reduced. Furthermore, the number of patients who can receive this test at any facility can be increased. This position may also be applicable in myocardial scintigraphy using some other tracers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Germano G, Chua T, Kiat H, Areeda JS, Berman DS. A quantitative phantom analysis of artifacts due to hepatic activity in technetium-99m myocardial perfusion SPECT studies.J Nucl Med 1994; 35: 356–359.
Munch G, Neverve J, Matsunari I, Schroter G, Schwaiger M. Myocardial technetium-99m-tetrofosmin and technetium-99m-sestamibi kinetics in normal subjects and patients with coronary artery disease.J Nucl Med 1997; 38: 428–432.
Hatton RL, Hutton BF, Angelides S, Choong KK, Larcos G. Improved tolerance to missing data in myocardial perfusion SPECT using OSEM reconstruction.Eur J Nucl Med 2004; 31:857–861.
Pretorius PH, Narayanan MV, Dahlberg ST, Leppo JA, King MA. The influence of attenuation and scatter compensation on the apparent distribution of Tc-99m sestamibi in cardiac slices.J Nucl Cardiol 2001; 8: 356–364.
Bai J, Hashimoto J, Suzuki T, Nakahara T, Kubo A, Iwanaga S, et al. Comparison of image reconstruction algorithms in myocardial perfusion scintigraphy.Ann Nucl Med 2001; 15: 79–83.
Lewin HC, Hyun M, DePuey EG, Schisterman E. Validation of a very rapid rest/stress 1 day 99mTc sestamibi stress protocol. Proceedings to ASNC 2003.
Binetti G, Senni M, Colombo F, Tasca G, Mamprin F, Caporale R, et al. Medical treatment of end-stage heart failure.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 1996; Suppl 2: 617–622.
Kubo A, Nakamura K, Sanmiya T, Shimizu S, Hashimoto S, Iwanaga S, et al. Phase I clinical study on99mTc-MIBI.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 1991; 28: 1133–1142.
Kubo A, Nakamura K, Hashimoto J, Sammiya T, Iwanaga S, Hashimoto S, et al. Phase I clinical trial of a new myocardial imaging agent,99mTc-PPN1011.KAKU IGAKU (Jpn J Nucl Med) 1992; 29: 1165–1176.
Nakajima K, Shuke N, Taki J, Ichihara T, Motomura N, Bunko H, et al. A Simulation of Dynamic SPECT Using Radiopharmaceuticals with Rapid Clearance.J Nucl Med 1992; 33: 1200–1206.
Liu Y-H, Lam PT, Sinusas AJ, Wackers FJT. Differential Effect of 180 and 360 Acquisition Orbits on the Accuracy of SPECT Imaging: Quantitative Evaluation in Phantoms.J Nucl Med 2002; 43: 1115–1124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monzen, H., Hirata, M., Nakanishi, A. et al. Exploring a technique for reducing the influence of scattered rays from surrounding organs to the heart during myocardial perfusion scintigraphy with technetium-99m sestamibi and technetium-99m tetrofosmin. Ann Nucl Med 20, 705–710 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984684
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984684