TABLE 1
Mathematic Notations and Definitions
| Notation | Definition |
| B2 | The transmission factor for radiation emanating from compartment 2 (thyroid) |
| d1 | The distance (m) to a bystander from the patient’s skin at the extrathyroidal source |
| d2 | The distance (m) to a bystander from the patient’s skin at the thyroid |
| Δd1 | The depth in the patient (m) of the extrathyroidal line source |
| Δd2 | The depth in the patient (m) of the thyroidal point source |
 | The fraction of administered isotope initially partitioned into compartment 1 |
 | The fraction of administered isotope initially partitioned into compartment 2 |
| gi | The perpendicular distance from the cylinder’s ith line source to the dose point |
| Δgi | The perpendicular distance from the cylinder’s ith line source to the cylinder’s surface in the direction of the dose point |
| HVL | The broad-beam half-value layer in water (m) of 131I’s 364-keV photon (the value 0.1 m is used, reference (9)) |
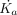 | The air kerma rate at the position of a bystander resulting from patient emanations |
 | The total air kerma at the position of a bystander beginning at a start time ts |
| l | Variable of integration, distance from midpoint of a line source to line source element dl |
| L | The length (m) of the line source |
 | The amount of isotope remaining in metabolic compartment 1 (extrathyroid) at time t |
 | The amount of isotope remaining in metabolic compartment 2 (thyroid) at time t |
 | The amount of isotope in the bladder at time t when the previous urination was at time T |
 | The amount of isotope remaining in the patient at time t (parallel model) |
 | The amount of isotope initially administered |
 | The effective half-life for the radioisotope leaving metabolic compartment 1 |
 | The effective half-life for the radioisotope leaving metabolic compartment 2 |
| Toc | The occupancy factor, that is, the average fraction of time that a specific bystander is present at a specified location |
| ts | The time that a family member or other bystander begins exposure to the patient’s radiation field |
| Γ | The air kerma rate constant (mGy/h/MBq at 1 m) for the radioisotope (the value 5.1613E−5 is used for 131I) |
 | The rate constant for the radioisotope leaving a metabolic compartment by nuclear decay |
 | The rate constant for the isotope leaving metabolic compartment 1 by biologic processes |
 | The rate constant for the isotope leaving metabolic compartment 2 by biologic processes |
 | The effective rate constant for the isotope leaving metabolic compartment 1 |
 | The effective rate constant for the isotope leaving metabolic compartment 2 |
 | The relationship between rate constant and half-life, where ln(2) is the natural log of 2 |